Thyme essential oil potentials as a bactericidal and biofilm-preventive agent against prevalent bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 40866486
- PMCID: PMC12391397
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-16485-5
Thyme essential oil potentials as a bactericidal and biofilm-preventive agent against prevalent bacterial pathogens
Abstract
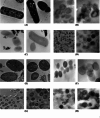
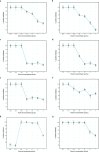
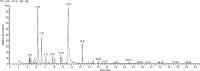
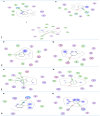
Antimicrobial resistance represents a significant global issue that requires the investigation of innovative approaches for infection management. In pursuit of alternative natural antimicrobials, nine plant essential oils were evaluated for their antibacterial properties against nine common bacterial pathogens. Among the tested essential oils, thyme essential oil demonstrated the highest antibacterial activity against all tested bacterial species, Thyme essential oil exhibited inhibition zones ranging from 17.3 to 51 mm with relative minimum inhibitory concentrations ranging from 99.2 to 450 µg/ml, implying the bactericidal effect. The ultrastructural changes in bacterial cells treated with thyme essential oil were visualized using transmission electron microscope. Thyme essential oil exhibited a potent inhibitory effect toward the biofilm formations for all the tested pathogenic strains. GC/MS analysis was used to determine the thyme essential oil composition. The major components of thyme essential oil were thymol (28.29%), o-cymene (18.31%), ç-terpinene (8.51%), eucalyptol (5%), linalool (2.86%), borneol (2.17%), á-myrcene (1.55%), à-pinene (1.52%) and camphene (1%). Molecular docking analysis demonstrated that the constituents present in the thyme essential oil had high binding affinity for ECF, FimH, LasR, PrfA and RhlA proteins, which were found to be associated with improved anti-biofilm efficacy. Furthermore, treatment with thyme essential oil led to the downregulation of essential genes associated with virulence and biofilm formation in the tested pathogens. These findings suggest that thyme essential oil has promising potential as an antibacterial and a biofilm inhibitory agent to combat bacterial infections in food and pharmaceutical industries.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Biofilm; Chemical composition; Gene expression; Molecular docking; Pathogenic bacteria; Thyme essential oil.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Silbergeld, E. K., Graham, J. & Price, L. B. Industrial food animal production, antimicrobial resistance, and human health. Annu. Rev. Public. Health. 29, 151–169 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Liu, F., Du, L., Zhao, T., Zhao, P. & Doyle, M. P. Effects of phenyllactic acid as sanitizing agent for inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes biofilms. Food Control. 78, 72–78 (2017).
-
- Sharma, S., Kumar, S., Kumar, P. & Tripathi, V. N. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative pathogens, a fresh look. Microbe4, 100108 (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

