Bulgarian exploratory analysis of time from diagnosis to treatment of lung cancer patients (Beat) - a retrospective database study on the patient pathway and time from diagnosis to treatment
- PMID: 40866827
- PMCID: PMC12382172
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-14228-3
Bulgarian exploratory analysis of time from diagnosis to treatment of lung cancer patients (Beat) - a retrospective database study on the patient pathway and time from diagnosis to treatment
Abstract
Background: Globocan data for 2020 rank lung cancer as the third most common malignancy (12.1%) and the deadliest cancer (18.3%) in Bulgaria. The current study aims to analyze lung cancer patient pathways and time to treatment from diagnosis based on real-world data.
Methods: We conducted an observational database study based on the secondary use of data collected for other purposes for 3 years (2020-2022). The main outcomes of interest were time from diagnosis to therapy measured in days on national and regional levels, stratified by therapy type and year and number of newly diagnosed patients with lung cancer in each of the years for the observed period. Data were analyzed through descriptive statistics.
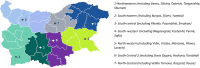
Results: Throughout the observed period, 8,585 patients were newly diagnosed with lung cancer, averaging approximately 2,861 diagnoses per year. Most patients' records reported non-small cell lung cancer (4536, 64%), Furthermore, most patients were diagnosed with advanced stages of cancer, with 61% (4297) being diagnosed with Stage IV. Time from Diagnosis to First Treatment (median) outcome showed variance by regions and type, from 7 to 40 days in the case of surgical treatment and 26 to 85 days in the case of combination therapy. The time from Diagnosis to First Systemic Treatment indicator shows a median delay between diagnosis to treatment of 42 days.
Conclusions: The study confirms that dynamic patient registers are crucial for performing real-world studies of treatment patterns and identifying gaps and inequities on a national level. There is a significant need to address the lack of screening programs for lung cancer in Bulgaria and ensure more equitable distribution of oncology centers.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Lung cancer; Patient pathway; Real-world data; Time to treatment.
© 2025. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates, and the Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. The data collection and analysis scope excluded safety and patient involvement reconciliation; therefore, informed ethical permission was not required for the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Global cancer observatory. Cancer today. Globocan: 2022: Bulgaria. Available at: https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/populations/100-bulga.... Accessed on: March 2024.
-
- Krzyszczyk P, Acevedo A, Davidoff EJ, Timmins LM, Marrero-Berrios I, Patel M, White C, Lowe C, Sherba JJ, Hartmanshenn C, O’Neill KM, Balter ML, Fritz ZR, Androulakis IP, Schloss RS, Yarmush ML. The growing role of precision and personalized medicine for cancer treatment. Technology (Singap world Sci). 2018 Sep-Dec;6(3–4):79–100. 10.1142/S2339547818300020 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maria Dimitrova P, Milushewa E, Petrova D, Mihaylova NT, Guenka Petrova. Triple negative breast cancer in Bulgaria: epidemiological data and treatment patterns based on real world evidence and patient registries. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2021;35(1):551–9. 10.1080/13102818.2021.1903338.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical