Combining Coronal and Axial DWI for Accurate Diagnosis of Brainstem Ischemic Strokes: Volume-Based Correlation with Stroke Severity
- PMID: 40867156
- PMCID: PMC12384511
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci15080823
Combining Coronal and Axial DWI for Accurate Diagnosis of Brainstem Ischemic Strokes: Volume-Based Correlation with Stroke Severity
Abstract
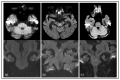
Background/Objectives: Brainstem ischemic strokes comprise 10% of ischemic strokes and are challenging to diagnose due to small lesion size and complex presentations. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is crucial for detecting ischemia, yet it can miss small lesions, especially when only axial slices are employed. This study investigated whether ischemic lesions visible in a single imaging plane correspond to smaller volumes and whether coronal DWI enhances detection compared to axial DWI alone. Methods: This retrospective single-center study examined 134 patients with brainstem ischemic strokes between December 2018 and November 2023. All patients underwent axial and coronal DWI. Clinical data, NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores, and modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores were recorded. Diffusion-restricted lesion volumes were calculated using multiple models (planimetric, ellipsoid, and spherical), and lesion visibility per imaging plane was analyzed. Results: Brainstem ischemic strokes were detected in 85.8% of patients. Coronal DWI alone identified 6% of lesions that were undetectable on axial DWI; meanwhile, axial DWI alone identified 6.7%. Combining both improved overall sensitivity to 86.6%. Ischemic lesions visible in only one plane were significantly smaller across all volume models. Higher NIHSS scores were strongly correlated with larger diffusion-restricted lesion volumes. Coronal DWI correlated better with clinical severity than axial DWI, especially in the midbrain and medulla. Conclusions: Coronal DWI significantly improves the detection of small brainstem infarcts and should be incorporated into routine stroke imaging protocols. Infarcts visible in only one plane are typically smaller, yet still clinically relevant. Combined imaging enhances diagnostic accuracy and supports early and precise intervention in posterior circulation strokes.
Keywords: axial DWI; brainstem ischemic stroke; coronal DWI; diffusion-weighted image (DWI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Narisawa A., Shamoto H., Shimizu H., Tominaga T., Yoshimoto T. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in acute brain stem infarction. No Shinkei Brain Nerve. 2001;53:1021–1026. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

