Methylphenidate as a Novel Adjunct in Opioid-Taking Patients: Insights into Dopaminergic Neuroadaptation and Hypoactive Delirium
- PMID: 40867181
- PMCID: PMC12385169
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci15080850
Methylphenidate as a Novel Adjunct in Opioid-Taking Patients: Insights into Dopaminergic Neuroadaptation and Hypoactive Delirium
Abstract
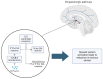
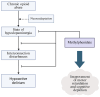
Background and aim of this review: The ongoing opioid epidemic underscores the urgent need for innovative pharmacological and behavioral interventions to mitigate the impact of opioid use disorder (OUD). This review aims to explore theoretical overlaps between the neurobiological mechanisms underlying OUD development and the pharmacodynamic profile of methylphenidate (MPH). Particular attention is given to the potential shared molecular targets, safety considerations, and therapeutic implications of MPH use in this clinical context. Main finding: In the development of opioid dependence, the negative reinforcement of the dopaminergic transmission of the mesocorticolimbic pathway induced by the supraspinal action of opioid receptor agonists plays a major role. The induced state of hypodopaminergic and hyperadrenergic modulates the underlying disease process by affecting cognitive control, affective regulation, and motivational drive. MPH, acting as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor and modulator of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT-2), increases extracellular dopamine availability and enhances dopaminergic signaling, suggesting potential utility in restoring dopaminergic tone in OUD. Additionally, MPH has shown efficacy in hypoactive delirium in patients with terminal cancer, improving both cognitive function and psychomotor drive. Conclusions and future perspectives: There appear to be converging neurobiological mechanisms between the action of MPH and the pathophysiology of OUD, particularly within the dopaminergic system. However, well-designed clinical trials are essential to identify the patient subgroups that may benefit from adjunctive MPH treatment, to evaluate its efficacy in this setting, and to assess the long-term safety and risk profile of stimulant use in individuals with OUD.
Keywords: dopaminergic neuroadaptation; mesolimbic reward system; methylphenidate; opioid use disorder; opioid withdrawal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Stimulant and non-stimulant drug therapy for people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 13;7(7):CD013136. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013136.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35844168 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Pain Assessment.2025 Jun 22. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 22. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32310558 Free Books & Documents.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

