The Surgical Imprint: How Operative Trauma May Shape Radiation Tolerance After Prostatectomy
- PMID: 40867315
- PMCID: PMC12385124
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17162685
The Surgical Imprint: How Operative Trauma May Shape Radiation Tolerance After Prostatectomy
Abstract
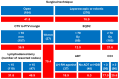
In a recent multicenter analysis of 454 patients undergoing post-prostatectomy salvage radiotherapy, the open surgical approach, as opposed to minimally invasive surgery, emerged, unexpectedly, as the strongest predictor of acute gastrointestinal and genitourinary toxicity. Patients treated with laparoscopic or robotic prostatectomy experienced significantly lower rates of ≥grade 2 toxicity compared to those who had undergone open retropubic surgery, irrespective of total dose, treatment margins, or radiation delivery platform. This finding, which to our knowledge has not been previously reported, raises the hypothesis that surgical technique leaves a lasting biological imprint on irradiated tissues. Drawing on current knowledge in radiobiology, cytokine signaling, wound healing, and pelvic dosimetry, we explore potential mechanisms by which open surgery may create a more hypoxic, inflamed, and fibrotic microenvironment, thereby amplifying radiation damage. We further discuss how target volume margins may biologically interact with this tissue state to increase normal tissue exposure. This Perspective aims to provide a conceptual framework for understanding this unexpected association, highlighting its clinical relevance for individualizing margins, counselling high-risk patients, and designing future studies at the interface of surgery and radiation oncology. This paper does not introduce additional patients or statistical models; instead, it offers an in-depth clinical and mechanistic interpretation of previously published ICAROS findings.
Keywords: CTV–PTV margin; acute toxicity; gastrointestinal toxicity; genitourinary toxicity; minimally invasive surgery; open prostatectomy; post-prostatectomy radiotherapy; radiosensitivity; salvage radiotherapy; surgical trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Interventions to reduce acute and late adverse gastrointestinal effects of pelvic radiotherapy for primary pelvic cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 23;1(1):CD012529. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012529.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29360138 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Anterior Approach Total Ankle Arthroplasty with Patient-Specific Cut Guides.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2025 Aug 15;15(3):e23.00027. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00027. eCollection 2025 Jul-Sep. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2025. PMID: 40821726 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics and antiseptics for surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 29;3(3):CD011712. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011712.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27021482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cornford P., van den Bergh R.C.N., Briers E., Van den Broeck T., Brunckhorst O., Darraugh J., Eberli D., De Meerleer G., De Santis M., Farolfi A., et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2024 Update. Part I: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2024;86:148–163. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.03.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eastham J.A., Auffenberg G.B., Barocas D.A., Chou R., Crispino T., Davis J.W., Eggener S., Horwitz E.M., Kane C.J., Kirkby E., et al. Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO Guideline. Part III: Principles of Radiation and Future Directions. J. Urol. 2022;208:26–33. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002759. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thompson I.M., Tangen C.M., Paradelo J., Lucia M.S., Miller G., Troyer D., Messing E., Forman J., Chin J., Swanson G., et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy for pathological T3N0M0 prostate cancer significantly reduces risk of metastases and improves survival: Long-term followup of a randomized clinical trial. J. Urol. 2009;181:956–962. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.11.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolla M., van Poppel H., Tombal B., Vekemans K., Da Pozzo L., de Reijke T.M., Verbaeys A., Bosset J.F., van Velthoven R., Colombel M., et al. Postoperative radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy for high-risk prostate cancer: Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial (EORTC trial 22911) Lancet. 2012;380:2018–2027. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61253-7. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

