MR-Guided Radiation Therapy for Prostate and Pancreas Cancer Treatment: A Dosimetric Study Across Two Major MR-Linac Platforms
- PMID: 40867337
- PMCID: PMC12384352
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17162708
MR-Guided Radiation Therapy for Prostate and Pancreas Cancer Treatment: A Dosimetric Study Across Two Major MR-Linac Platforms
Abstract
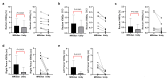
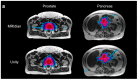
Background/Objectives: MR-guided radiation therapy (MRgRT) has rapidly evolved into an important treatment modality, with the Elekta Unity and ViewRay MRIdian systems being two major MR-linac platforms. Despite the shared concept of MRgRT, the two platforms elected different system designs that could potentially impact the dosimetric characteristics and quality of a treatment. In this study, we aim to perform a comparative dosimetric investigation between these two MR-linac systems in prostate and pancreas cancers. Methods: Dosimetric characteristics were evaluated by retrospectively re-creating 20 clinical prostate and pancreas cases originally treated on MRIdian using the Unity system, adhering to MIRAGE and SMART clinical trial constraints. Treatment plans were re-created with matching planning images, structures, beam geometry, and dose parameters. To ensure comparison consistency, all Unity treatment plans were normalized to match the target coverage of the MRIdian counterparts, and the organ-at-risk (OAR) dose was investigated. Results: Most OARs' dose-volume metrics showed no statistically significant differences. For prostate patients, Unity demonstrated lower rectum V36Gy (p = 0.0095), V38Gy (p = 0.0043), V40Gy (p = 0.0469), and lower left (p = 0.0137) and right femur V20Gy (p = 0.0020). For pancreas patients, Unity plans had a lower mean liver dose (p = 0.0371). All Unity plans had a Gamma passing rate > 90%, confirming the clinical deliverability. Mean delivery times were 12.78 ± 1.68 and 13.53 ± 1.88 min for MRIdian and Unity prostate plans, respectively, and 14.58 ± 2.78 and 17.40 ± 3.77 min for MRIdian and Unity pancreas plans, respectively. Conclusions: Overall, comparable treatment quality and delivery times were observed between the two platforms.
Keywords: MR-guided radiation therapy; MR-linac; SBRT; dosimetric comparison; pancreas cancer; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
H.D. Conflict of Interest: None; J.P. Conflict of Interest: None; M.V.L. Conflict of Interest: None; C.A. Conflict of Interest: None; B.S. Conflict of Interest: Employee of Elekta USA; P.B. Conflict of Interest: Employee of Elekta USA; J.D. Conflict of Interest: Employee of Elekta USA; M.S. Conflict of Interest: Employee of Elekta USA; A.K. Conflict of Interest: a consulting relationship with Varian, research funding from Lantheus, Janssen, Point Biopharma and Artera AI, honoraria for lectures, presentations or educational events from Varian and Accuray, participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board with Novartis, Lantheus, Janssen and Boston Scientific; A.R. Conflict of Interest: None; X.Q. Conflict of Interest: grants or contracts from Varian, and deputy editorship for the journal of Medical Physics; D.H. Conflict of Interest: a consulting relationship with Elekta, research funding from Elekta, and royalties from IBA; J.L. Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures



References
-
- Almansour H., Afat S., Fritz V., Schick F., Nachbar M., Thorwarth D., Zips D., Müller A.-C., Nikolaou K., Othman A.E., et al. Prospective Image Quality and Lesion Assessment in the Setting of MR-Guided Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer on an MR-Linac at 1.5 T: A Comparison to a Standard 3 T MRI. Cancers. 2021;13:1533. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071533. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanescu T., Shessel A., Carpino-Rocca C., Taylor E., Semeniuk O., Li W., Barry A., Lukovic J., Dawson L., Hosni A. MRI-Guided Online Adaptive Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy of Liver and Pancreas Tumors on an MR-Linac System. Cancers. 2022;14:716. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030716. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen H.-Y., Larson P.E.Z., Bok R.A., von Morze C., Sriram R., Delos Santos R., Delos Santos J., Gordon J.W., Bahrami N., Ferrone M., et al. Assessing Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness with Hyperpolarized Dual-Agent 3D Dynamic Imaging of Metabolism and Perfusion. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3207–3216. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

