Hypoxia Exacerbates Inflammatory Signaling in Human Coronavirus OC43-Infected Lung Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 40867589
- PMCID: PMC12384405
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15081144
Hypoxia Exacerbates Inflammatory Signaling in Human Coronavirus OC43-Infected Lung Epithelial Cells
Abstract
Cytokine storm (CS) is associated with poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients. Hypoxic signaling has been proposed to influence proinflammatory pathways and to be involved in the development of CS. Here, for the first time, the role of hypoxia in coronavirus-mediated inflammation has been investigated, using transcriptomic and proteomic approaches. Analysis of the transcriptome of A549 lung epithelial cells using RNA sequencing revealed 191 mRNAs which were synergistically upregulated and 43 mRNAs which were synergistically downregulated by the combination of human Betacoronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) infection and hypoxia. Synergistically upregulated mRNAs were strongly associated with inflammatory pathway activation. Analysis of the expression of 105 cytokines and immune-related proteins using antibody arrays identified five proteins (IGFBP-3, VEGF, CCL20, CD30, and myeloperoxidase) which were markedly upregulated in HCoV-OC43 infection in hypoxia compared to HCoV-OC43 infection in normal oxygen conditions. Our findings show that COVID-19 patients with lung hypoxia may face increased risk of inflammatory complications. Two of the proteins we have identified as synergistically upregulated, the cytokines VEGF and CCL20, represent potential future therapeutic targets. These could be targeted directly or, based on the novel findings described here by inhibiting hypoxia signaling pathways, to reduce excessive inflammatory cytokine responses in patients with severe infections.
Keywords: CCL20; COVID-19; HCoV-OC43; IGFBP3; VEGF; cytokine storm; hypoxia; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

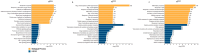


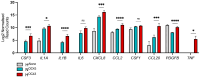

References
-
- Frisoni P., Neri M., D'Errico S., Alfieri L., Bonuccelli D., Cingolani M., Di Paolo M., Gaudio R.M., Lestani M., Marti M., et al. Cytokine storm and histopathological findings in 60 cases of COVID-19-related death: From viral load research to immunohistochemical quantification of major players IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-15 and TNF-alpha. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2022;18:4–19. doi: 10.1007/s12024-021-00414-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferrara J.L., Abhyankar S., Gilliland D.G. Cytokine storm of graft-versus-host disease: A critical effector role for interleukin-1. Transplant. Proc. 1993;25:1216–1217. - PubMed
-
- Ramatillah D.L., Gan S.H., Pratiwy I., Syed Sulaiman S.A., Jaber A.A.S., Jusnita N., Lukas S., Abu Bakar U. Impact of cytokine storm on severity of COVID-19 disease in a private hospital in West Jakarta prior to vaccination. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0262438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

