Well-Being of the Baltic Herring and Bycatch Fish Species from FAO Major Fishing Areas 27 According to Microplastic Pollution
- PMID: 40867710
- PMCID: PMC12382631
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15162381
Well-Being of the Baltic Herring and Bycatch Fish Species from FAO Major Fishing Areas 27 According to Microplastic Pollution
Abstract
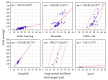
Condition factors are essential in fishery science. They provide insights into fish well-being according to the impact of environmental stressors. The Fulton condition factor (K) and hepatosomatic index (HSI), as well as two new indices (GILSI and GITI), were used to assess the well-being of herring and bycatch species (cod, flounder, sprat, long-spined bullhead, lumpfish) from the Baltic Sea. For Cyclopterus lumpus and Taurulus bubalis, K and HSI values were reported for the first time. Fish from different basins differed according to biometric measures (weight: 6.09-750.12 g; length: 8.6-41.8 mm) and condition indices (mean K: 1.19; HSI: 0.02; GITI: 0.04; GILSI: 0.03). Microplastics (MPs) were found in all species (21% (sprat)-79% (lumpfish)), averaging 3.1 items/fish. The organ-wise analysis revealed that 46% of the gills, 16% of the livers, and 38% of the gastrointestinal tracts were contaminated with MPs. The relationship between these indices and MPs abundance in the organs of herring was examined using PCA, revealing a negative impact of MPs on fish health. The morphometric features and the chemical composition of MPs were also detected. The dominant size ranges were 0.11-0.5 mm (30%) and 1.01-5 mm (28%). Blue fibers were the most common.
Keywords: Baltic cod; biometric features; flounder; long-spined bullhead; lumpfish; pollution with microplastics; principal component analysis; sprat; the Baltic Sea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Holmlund C., Hammer M. Ecological ecosystem services generated by fish populations. Ecol. Econ. 1999;29:253–268. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00015-4. - DOI
-
- Sterner R.W., Elser J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press; Princeton, NJ, USA: 2002. Stoichiometry and homeostasis; pp. 1–43. - DOI
-
- Schiettekatte N.M.D., Casey J.M., Brandl S.J., Mercière A., Degregori S., Burkepile D., Van Wert J.C., Ghilardi M., Villéger S., Parravicini V. The role of fish feces for nutrient cycling on coral reefs. Oikos. 2023;9:e09914. doi: 10.1111/oik.09914. - DOI
-
- Whitfield A.K. Fishes and the environmental status of South African estuaries. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 1996;3:45–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2400.1996.tb00129.x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

