Protective Effects of Luteolin on Glaesserella parasuis-Induced Injury: An In Vitro Study with Porcine Vascular Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 40868017
- PMCID: PMC12383133
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14080824
Protective Effects of Luteolin on Glaesserella parasuis-Induced Injury: An In Vitro Study with Porcine Vascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
Background:Glaesserella parasuis (GPS) is a conditional pathogen that colonizes the upper respiratory tract in pigs and causes Glässer's disease, resulting in high morbidity and mortality in piglets. GPS infection increases the vascular endothelial permeability, but the mechanism has not been fully elucidated. Luteolin (Lut) is a naturally occurring flavonoid found in plants such as vegetables, herbs, and fruits, but its potential to treat the increased vascular endothelial permeability caused by GPS infection has not been evaluated. Results: This study revealed that GPS infection induces increased vascular endothelial permeability in porcine iliac artery endothelial cells (PIECs) by increasing the gene expressions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-8, and IL-1β, and by regulating F-actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Mechanistically, GPS infection or Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) overexpression significantly increased the expressions of vascular-endothelial-permeability-related proteins (CD44; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA); matrixmetalloProteinase-3 (MMP-3); MMP-9; and SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase (c-Src)) and increased the vascular endothelial permeability; these changes were alleviated by a Lut treatment or CD44 silencing in the PIECs. Conclusions: This study comprehensively illustrates the potential targets and molecular mechanism of Lut in alleviating the GPS-induced increase in vascular endothelial permeability. The CD44 pathway and Lut may be an effective target and antibiotic alternative, respectively, to prevent the increased vascular endothelial permeability caused by GPS.
Keywords: CD44; Glaesserella parasuis; infection; luteolin; vascular endothelial permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
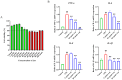

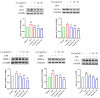


References
-
- Huang A., Huang X., Zhang Z., Yuan Z., Huang L., Wang Y., Tao Y., Chen D., Liu Z., Hao H. Dosing regimen of aditoprim and sulfamethoxazole combination for the Glaesserella parasuis containing resistance and virulence genes. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:2058. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fu S., Liu J., Xu J., Zuo S., Zhang Y., Guo L., Qiu Y., Ye C., Liu Y., Wu Z., et al. The effect of baicalin on microRNA expression profiles in porcine aortic vascular endothelial cells infected by Haemophilus parasuis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020;472:45–56. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03782-y. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

