Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures
- PMID: 40868045
- PMCID: PMC12384009
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13081789
Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures
Abstract
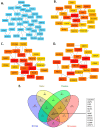
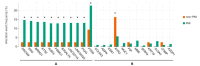
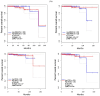
Background: Prostate cancer is a common malignancy among men worldwide, with various histopathologic features that influence its progression and prognosis. One such feature is perineural invasion (PNI), which has been associated with aggressive disease. In this retrospective study, we analyzed genomic alterations associated with PNI in patients who underwent radical prostatectomy. Methods: A total of 421 prostate cancer patients who underwent radical prostatectomy without neoadjuvant therapy were identified from The Cancer Genome Atlas. PNI was present in 378 patients (89.8%) and absent in 43 (10.2%). Differentially expressed genes were identified, and mRNA expression levels of key genes were analyzed. The prognostic significance of these genes was evaluated using log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazards models to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals. Results: Levels of COL9A3, ASPN, ESR1, MUC1, PIP, SFRP4, KRT19, CLDN1, and COMP were significantly higher in the tumor tissues of patients in the PNI group compared to those in the non-PNI group (q < 0.05), and RYR2, MME, and AZGP1 expression levels were significantly higher in the non-PNI group (q < 0.05). A high mRNA expression level of AZGP1 was associated with longer disease-free survival, whereas high mRNA expressions of ASPN, COMP, RYR2, and SFRP4 were associated with shorter disease-free survival. Conclusions: Prostate cancer patients with genomic alterations associated with PNI may face a higher risk of disease progression after prostatectomy, highlighting the need for further prospective studies to validate these findings.
Keywords: perineural invasion; prognostic biomarkers; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Cozzi G., Rocco B.M., Grasso A., Rosso M., Abed El Rahman D., Oliva I., Talso M., Costa B., Tafa A., Palumbo C., et al. Perineural invasion as a predictor of extraprostatic extension of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. J. Urol. 2013;47:443–448. doi: 10.3109/21681805.2013.776106. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

