Analyzing Retinal Vessel Morphology in MS Using Interpretable AI on Deep Learning-Segmented IR-SLO Images
- PMID: 40868360
- PMCID: PMC12384046
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12080847
Analyzing Retinal Vessel Morphology in MS Using Interpretable AI on Deep Learning-Segmented IR-SLO Images
Abstract
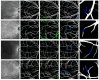
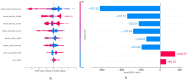
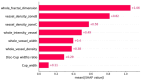
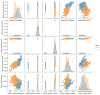
Multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic disease of the central nervous system, is known to cause structural and vascular changes in the retina. Although optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus photography can detect retinal thinning and circulatory abnormalities, these findings are not specific to MS. This study explores the potential of Infrared Scanning-Laser-Ophthalmoscopy (IR-SLO) imaging to uncover vascular morphological features that may serve as MS-specific biomarkers. Using an age-matched, subject-wise stratified k-fold cross-validation approach, a deep learning model originally designed for color fundus images was adapted to segment optic disc, optic cup, and retinal vessels in IR-SLO images, achieving Dice coefficients of 91%, 94.5%, and 97%, respectively. This process included tailored pre- and post-processing steps to optimize segmentation accuracy. Subsequently, clinically relevant features were extracted. Statistical analyses followed by SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) identified vessel fractal dimension, vessel density in zones B and C (circular regions extending 0.5-1 and 0.5-2 optic disc diameters from the optic disc margin, respectively), along with vessel intensity and width, as key differentiators between MS patients and healthy controls. These findings suggest that IR-SLO can non-invasively detect retinal vascular biomarkers that may serve as additional or alternative diagnostic markers for MS diagnosis, complementing current invasive procedures.
Keywords: deep learning; feature extraction; feature importance; machine learning; multiple sclerosis; scanning laser ophthalmoscopy; segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SLO-Net: Enhancing Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis Beyond Optical Coherence Tomography Using Infrared Reflectance Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Images.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Jul 1;13(7):13. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.7.13. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39017629 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglion Cell Layer Thickness as a Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Outcome: An OCT study.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr-Jun;69(2):200-207. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2025.32. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40698100 Free PMC article.
-
SLOctolyzer: Fully Automatic Analysis Toolkit for Segmentation and Feature Extracting in Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Images.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Nov 4;13(11):7. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.11.7. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39514218 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for diagnosing exudative age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 17;10(10):CD015522. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015522.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39417312
-
Optic nerve head and fibre layer imaging for diagnosing glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 30;2015(11):CD008803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26618332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kashani A.H., Asanad S., Chan J.W., Singer M.B., Zhang J., Sharifi M., Khansari M.M., Abdolahi F., Shi Y., Biffi A., et al. Past, present and future role of retinal imaging in neurodegenerative disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021;83:100938. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100938. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petzold A., Balcer L.J., Calabresi P.A., Costello F., Frohman T.C., Frohman E.M., Martinez-Lapiscina E.H., Green A.J., Kardon R., Outteryck O., et al. Retinal layer segmentation in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:797–812. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30278-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Costanzo E., Lengyel I., Parravano M., Biagini I., Veldsman M., Badhwar A., Betts M., Cherubini A., Llewellyn D.J., Lourida I., et al. Ocular Biomarkers for Alzheimer Disease Dementia: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023;141:84–91. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.4845. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

