Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Jackfruit Peel Carboxymethylcellulose/Graphene Oxide/Kaolin Composite Hydrogels
- PMID: 40868757
- PMCID: PMC12385731
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11080626
Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Jackfruit Peel Carboxymethylcellulose/Graphene Oxide/Kaolin Composite Hydrogels
Abstract
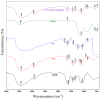
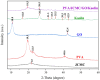
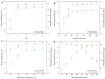
This study presents an environmentally benign composite hydrogel system by combining polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with carboxymethyl cellulose derived from jackfruit peel waste (JCMC), subsequently reinforced with graphene oxide (GO) and Kaolin nanoparticles for enhanced Congo red (CR) adsorption. The structural properties of the synthesized hydrogels were comprehensively characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). FTIR analysis confirmed hydrogel formation through hydrogen bonding interactions, while XRD and SEM revealed the uniform dispersion of GO and Kaolin within the polymer matrix, resulting in an improved adsorption performance. Furthermore, the adsorption efficiency of the composite hydrogels was systematically evaluated under varying conditions, including solution pH, contact time, temperature, and initial CR concentration. Optimal CR removal (92.3%) was achieved at pH 8.0, with equilibrium attained within 90 min. The adsorption kinetics were best fitted by the pseudo-second-order model (R2 = 0.9998), confirming a chemisorption-dominated process. The equilibrium adsorption data were accurately described by the Langmuir isotherm model, indicating monolayer coverage with an exceptional maximum capacity of 200.80 mg/g. These findings highlight the superior adsorption performance of the PVA/JCMC/GO/Kaolin hydrogels, attributed to their tailored physicochemical properties and synergistic interactions among components. This study offers both sustainable jackfruit peel waste valorization and an effective solution for anionic dye removal in wastewater treatment.
Keywords: Congo red adsorption; carboxymethyl cellulose; composite hydrogels; graphene oxide; jackfruit peel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Jin L., Qian T., Cheng Y., Qi D., Xin J.H., Xia G., Cui Z. Synthesis, recovery, and application of environmentally friendly disperse dyes with high light fastness. Text Res. J. 2024;94:566–582. doi: 10.1177/00405175231208023. - DOI
-
- Uduma R.C., Oguzie K.L., Chijioke C.F., Ogbulie T.E., Oguzie E.E. Bioelectrochemical technologies for simultaneous treatment of dye wastewater and electricity generation: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023;20:10415–10434. doi: 10.1007/s13762-022-04753-0. - DOI
-
- Karaday M., Güllüce E., Ahin Y.G., Olak L., Karaday G.K.E., Aksu E., Güllüce M. Molecular docking assisted toxicity assessment of congo red and detoxification potential of Fraxinus excelsior L. (Oleaceae) biosorbent application. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2025;25:6842–6849. doi: 10.1007/s13399-025-06842-9. - DOI
-
- Zinatloo-Ajabshir S., Rakhshani S., Mehrabadi Z., Farsadrooh M., Feizi-Dehnayebi M., Rakhshani S., Duek M., Eigner V., Rtimi S., Aminabhavi T.M. Novel rod-like [Cu(phen)2(OAc)]·PF6 complex for high-performance visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of hazardous organic dyes: DFT approach, Hirshfeld and fingerprint plot analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2025;350:119545. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119545. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

