Comorbidities Across Functional Neurological Disorder Subtypes: A Comprehensive Narrative Synthesis
- PMID: 40868970
- PMCID: PMC12387761
- DOI: 10.3390/life15081322
Comorbidities Across Functional Neurological Disorder Subtypes: A Comprehensive Narrative Synthesis
Abstract
Background: Functional Neurological Disorder (FND) encompasses a spectrum of symptoms-including motor, cognitive, and seizure-like manifestations-that are not fully explained by structural neurological disease. Accumulating evidence suggests that comorbid psychiatric and somatic conditions significantly influence the clinical course, diagnostic complexity, and treatment response in FND.
Objective: This study systematically explores psychiatric and medical comorbidities across major FND subtypes-Functional Cognitive Disorder (FCD), Functional Movement Disorder (FMD), and Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures (PNES)-with an emphasis on subtype-specific patterns and shared vulnerabilities.
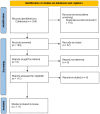
Methods: We conducted a narrative review of the published literature, guided by systematic principles for transparency, covering both foundational and contemporary sources to examine comorbid conditions in patients with FCD, FMD, PNES, PPPD and general (mixed) FND populations. Relevant studies were identified through structured research and included based on methodological rigor and detailed reporting of comorbidities (PRISMA). Extracted data were organized by subtype and comorbidity type (psychiatric or medical/somatic).
Results: Across all FND subtypes, high rates of psychiatric comorbidities were observed, particularly depression, anxiety, PTSD, and dissociative symptoms. FCD was predominantly associated with internalizing symptoms, affective misattribution, and heightened cognitive self-monitoring. FMD demonstrated strong links with trauma, emotional dysregulation, and personality vulnerabilities. PNES was characterized by the highest burden of psychiatric illness, with complex trauma histories and dissociation frequently reported. Somatic comorbidities-such as fibromyalgia, chronic pain, irritable bowel syndrome, and fatigue-were also prevalent across all subtypes, reflecting overlapping mechanisms involving interoception, central sensitization, and functional symptom migration.
Conclusions: Comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions are integral to understanding the presentation and management of FND. Subtype-specific patterns underscore the need for individualized diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, while the shared biopsychosocial mechanisms suggest benefits of integrated care models across the FND spectrum.
Keywords: FCD; FMD; FND subtypes; functional neurological disorder; psychiatric comorbidities; somatic comorbidities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Functional Neurologic Disorder. 8 January 2024. [(accessed on 1 May 2025)]; Available online: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/functional-neurol....
-
- Charcot J.M. Leçons du Mardi à la Salpêtrière: Policliniques 1887–1888. Publications du Progrès Médical; Paris, France: 1887.
-
- Espay A.J., Aybek S., Carson A., Edwards M.J., Goldstein L.H., Hallett M., LaFaver K., LaFrance W.C., Jr., Lang A.E., Nicholson T., et al. Current Concepts in Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Neurological Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75:1132–1141. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.1264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perez D.L., Nicholson T.R., Asadi-Pooya A.A., Bègue I., Butler M., Carson A.J., David A.S., Deeley Q., Diez I., Edwards M.J., et al. Neuroimaging in Functional Neurological Disorder: State of the Field and Research Agenda. NeuroImage Clin. 2021;30:102623. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102623. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources