Circulating FGF-21 as a Disease-Modifying Factor Associated with Distinct Symptoms and Cognitive Profiles in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis and Fibromyalgia
- PMID: 40868993
- PMCID: PMC12386925
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26167670
Circulating FGF-21 as a Disease-Modifying Factor Associated with Distinct Symptoms and Cognitive Profiles in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis and Fibromyalgia
Abstract
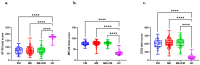
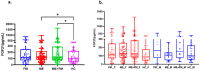
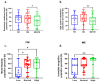
Myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) and fibromyalgia (FM) are overlapping syndromes characterized by persistent fatigue, cognitive difficulties, and post-exertional malaise (PEM), yet they lack objective biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21), a stress-responsive metabolic hormone, may offer a promising avenue to distinguish subtypes within these patient populations. In this cross-sectional study, plasma FGF-21 levels were measured in 250 patients (FM = 47; ME = 99; ME + FM = 104) and 54 healthy controls. Participants were categorized based on FGF-21 levels into three groups: low (0-50 pg/mL), normal (51-200 pg/mL), and high (>200 pg/mL). Symptoms burden and cognitive function were assessed using validated questionnaires (SF-36, MFI-20, DSQ, DPEMQ) and the BrainCheck platform. A standardized mechanical provocation maneuver was used to induce PEM. Results showed that elevated FGF-21 levels were frequently observed in ME and ME + FM but varied widely across all groups. Stratification by circulating FGF-21 levels, rather than diagnosis alone, revealed distinct symptom and cognitive profiles. Low FGF-21 levels were linked to worsened PEM perception in FM, increased PEM severity and immune/autonomic symptoms in ME, and poorer mental health in ME + FM. Conversely, high FGF-21 levels correlated with better cognition in ME but greater fatigue in ME + FM. These findings suggest that FGF-21 may serve as a valuable biomarker for identifying clinically meaningful subtypes within ME and FM, supporting the development of personalized treatments. Furthermore, discrepancies between DSQ and DPEMQ highlight the need for objective PEM assessment tools. Overall, FGF-21 shows potential as a biomarker to guide precision medicine in these complex conditions.
Keywords: FGF-21; biomarkers; cognition; fibromyalgia; myalgic encephalomyelitis; symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M. is the Director of the Interdisciplinary Canadian Collaborative Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ICanCME) Research Network, a national research network funded by The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (grant MNC—166242 and MNC—196095 to A.M.) and a Member of the Scientific Advisory Board of the Open Medicine Foundation (USA).
Figures
References
-
- Nacul L., O’Boyle S., Palla L., Nacul F.E., Mudie K., Kingdon C.C., Cliff J.M., Clark T.G., Dockrell H.M., Lacerda E.M. How Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) Progresses: The Natural History of ME/CFS. Front. Neurol. 2020;11:826. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00826. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

