Development of Emerin mRNA Lipid Nanoparticles to Rescue Myogenic Differentiation
- PMID: 40869095
- PMCID: PMC12386347
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26167774
Development of Emerin mRNA Lipid Nanoparticles to Rescue Myogenic Differentiation
Abstract
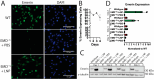
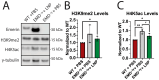
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 1 (EDMD1) arises from mutations in EMD. Most EDMD1 patients lack detectable emerin expression. They experience symptoms such as skeletal muscle wasting, joint contractures, and cardiac conduction defects. Currently, physicians rely on treating patient symptoms without addressing the underlying cause-lack of functional emerin protein. Thus, there is a need for therapeutic approaches that restore emerin protein expression to improve patient outcomes. One way would be to deliver emerin mRNA or protein directly to affected tissues to restore tissue homeostasis. Here, we evaluated the utility of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver emerin mRNA to diseased cells. LNPs have been studied for decades and have recently been used clinically for vaccination and treatment of a myriad of diseases. Here, we show that the treatment of emerin-null myogenic progenitors with LNPs encapsulating emerin mRNA causes robust emerin protein expression that persists for at least 4 days. The treatment of differentiating emerin-null myogenic progenitors with 2.5 pg/cell emerin LNPs significantly improved their differentiation. The toxicity profiling of emerin mRNA LNP (EMD-LNP) dosing shows little toxicity at the effective dose. These data support the potential use of EMD-LNPs as a viable treatment option and establishes its utility for studying EDMD pathology.
Keywords: EDMD; Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy; emerin; lipid nanoparticle; myogenic differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

