Multi-Layered Analysis of TGF-β Signaling and Regulation via DNA Methylation and microRNAs in Astrocytic Tumors
- PMID: 40869118
- PMCID: PMC12387059
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26167798
Multi-Layered Analysis of TGF-β Signaling and Regulation via DNA Methylation and microRNAs in Astrocytic Tumors
Abstract
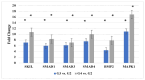
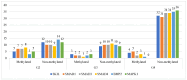
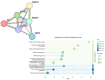
Astrocytic tumors are a heterogeneous group of glial neoplasms characterized by marked differences in biological behavior and patient prognosis. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling plays a pivotal role in astrocytoma pathogenesis; however, the extent and mechanisms of its epigenetic regulation remain poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate how promoter methylation and microRNA-mediated mechanisms regulate key genes within the TGF-β signaling pathway across various astrocytoma grades. Tumor tissue samples from 65 patients with WHO grade II-IV astrocytomas were analyzed using Affymetrix gene expression and microRNA microarrays. Promoter methylation of TGF-β signaling genes was assessed using methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP). Gene expression was validated by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), and protein levels were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). MicroRNA targets were predicted using bioinformatic tools, and survival analyses were conducted using Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression models. Six genes-SMAD1, SMAD3, SKIL, BMP2, SMAD4, and MAPK1-showed significant upregulation in high-grade tumors (fold change > 5.0, p < 0.05), supported by RT-qPCR and protein-level data. Promoter hypomethylation and reduced expression of regulatory microRNAs (e.g., hsa-miR-145-5p targeting SMAD3) were more common in higher-grade tumors. Protein-protein interaction analysis indicated strong functional interconnectivity among the overexpressed genes. High protein levels of SMAD1, SMAD3, and SKIL were significantly associated with shorter overall survival (p < 0.001). This multi-level analysis reveals that astrocytic tumor progression involves epigenetic derepression and microRNA-mediated dysregulation of TGF-β signaling. Elevated expression of SMAD1, SMAD3, and SKIL emerged as strong prognostic indicators, underscoring their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in astrocytic tumors.
Keywords: DNA methylation; MAPK1; SMAD proteins; TGF-β signaling; astrocytic tumors; epigenetic regulation; gene expression profiling; glioma; microRNA; prognostic biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the Expression Patterns of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Signaling Pathways and Regulatory MicroRNAs in Astrocytic Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5892. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125892. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565357 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics profiling of TGF-β isoforms and regulatory miRNAs in astrocytic tumors reveals TGF-β-3 as a prognostic biomarker.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 20;15:1592685. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1592685. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40620718 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX2 mediated epithelial mesenchymal transition induced by TGF beta and Smad signaling promotes malignant progression in glioma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 23;15(1):26781. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09167-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40702072 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of microRNA Expression and DNA Methylation in HPV-Related Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 26;25(23):12714. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312714. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684425 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cano-Valdez A.M., Sevilla-Lizcano D.B. Pathological Classification of Brain Tumors. In: Monroy-Sosa A., Chakravarthi S.S., De La Garza-Salazar J.G., Meneses Garcia A., Kassam A.B., editors. Principles of Neuro-Oncology. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 75–105.
-
- Machnik G., Bułdak Ł., Zapletal-Pudełko K., Grabarek B.O., Staszkiewicz R., Sobański D., Okopień B. The Impact of Wound-Healing Assay, Phorbol Myristate Acetate (PMA) Stimulation and siRNA-Mediated FURIN Gene Silencing on Endogenous Retroviral ERVW-1 Expression Level in U87-MG Astrocytoma Cells. Adv. Med. Sci. 2024;69:113–124. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2024.02.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

