Integrative High-Throughput RNAi Screening Identifies BRSK1, STK32C and STK40 as Novel Activators of YAP/TAZ
- PMID: 40869130
- PMCID: PMC12386767
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26167810
Integrative High-Throughput RNAi Screening Identifies BRSK1, STK32C and STK40 as Novel Activators of YAP/TAZ
Abstract
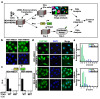
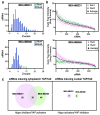
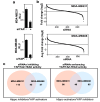
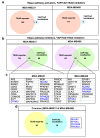
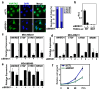
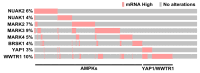
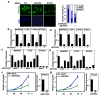
Disruption of the Hippo pathway leads to activation of the YAP/TAZ transcriptional program which promotes tumor initiation, progression and metastasis in diverse cancers. Aggressive triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) lack an effective therapy; thus, inactivating YAP and TAZ has emerged as an attractive approach and a new treatment modality. Thus, we performed two complementary high-throughput RNAi-based kinome screens to uncover cancer-associated activators of YAP/TAZ in two TNBC cell lines, MDA-MB231 and MDA-MB468. Integrated analysis that combined a YAP/TAZ localization screen with a TEAD-luciferase reporter screen, identified novel regulators including BRSK1, STK32C and STK40. The AMPK family members NUAKs, MARKs and SIKs are known to inhibit the Hippo kinase cassette; here, we uncover BRSK1, another AMPK family member as a regulator of YAP/TAZ. We also reveal that two poorly studied kinases, STK32C, a member of the AGC family, and STK40, a pseudokinase, can also inhibit the activity of YAP/TAZ. Thus, our studies expand the repertoire of known AMPK family members and reveal two new kinases that modulate the Hippo pathway and may play a role in YAP/TAZ driven breast cancers. Further analysis of other screen hits may similarly uncover new regulators that could be targeted for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: AMPK family members; BRSK1; Hippo pathway; RNAi screening; STK32C; STK40; YAP/TAZ; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

