Integrative Approaches to Myopathies and Muscular Dystrophies: Molecular Mechanisms, Diagnostics, and Future Therapies
- PMID: 40869293
- PMCID: PMC12386774
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26167972
Integrative Approaches to Myopathies and Muscular Dystrophies: Molecular Mechanisms, Diagnostics, and Future Therapies
Abstract
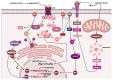
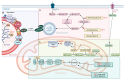
Myopathies and muscular dystrophies are a diverse group of rare or ultra-rare diseases that significantly impact patients' quality of life and pose major challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Despite their heterogeneity, many share common molecular mechanisms, particularly involving sarcomeric dysfunction, impaired autophagy, and disrupted gene expression. This review explores the genetic and pathophysiological foundations of major myopathy subtypes, including cardiomyopathies, metabolic and mitochondrial myopathies, congenital and distal myopathies, myofibrillar myopathies, inflammatory myopathies, and muscular dystrophies. Special emphasis is placed on the role of autophagy dysregulation in disease progression, as well as its therapeutic potential. We discuss emerging diagnostic approaches, such as whole-exome sequencing, advanced imaging, and muscle biopsy, alongside therapeutic strategies, including physiotherapy, supplementation, autophagy modulators, and gene therapies. Gene therapy methods, such as adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, CRISPR-Cas9, and antisense oligonucleotide, are evaluated for their promise and limitations. The review also highlights the potential of drug repurposing and artificial intelligence tools in advancing diagnostics and personalized treatment. By identifying shared molecular targets, particularly in autophagy and proteostasis networks, we propose unified therapeutic strategies across multiple myopathy subtypes. Finally, we discuss international research collaborations and rare disease programs that are driving innovation in this evolving field.
Keywords: drug repositioning; gene therapy; muscular diseases; myopathies; protein quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ferreira A., Ferreira V., Antunes M.M., Lousinha A., Pereira-da-Silva T., Antunes D., Cunha P.S., Oliveira M., Ferreira R.C., Rosa S.A. Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A Comprehensive Approach to Diagnosis and Risk Stratification. Biomedicines. 2023;11:834. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030834. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

