Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Silent Driver of Cardiovascular Risk and a New Target for Intervention
- PMID: 40869400
- PMCID: PMC12386202
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26168081
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Silent Driver of Cardiovascular Risk and a New Target for Intervention
Abstract
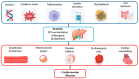
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) significantly increases the risk of steatohepatitis and cirrhosis and multiple extrahepatic complications, in particular, cardiometabolic disease, including type 2 diabetes, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD), and heart failure, with a significant negative impact on health-related quality of life, becoming a substantial economic burden. Moreover, cardiovascular events represent the leading cause of death in MASLD patients. A timely diagnosis stratifies patient for their risk. It can facilitate early lifestyle changes or pharmacological management of dysmetabolic conditions, thereby slowing disease progression, lowering cardiovascular risk, and preventing CVD and cirrhosis. In this narrative review, we will discuss the current knowledge on MASLD and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) pathophysiology, emphasizing their systemic nature, the link to CVD, and available and emerging treatment strategies.
Keywords: GIP-1; GLP-1 agonists; MASH; MASLD; cardiometabolic risk; cardiovascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MΑSLD).2025 Aug 9. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Aug 9. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31082077 Free Books & Documents.
-
Pharmacological treatment options for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review.Eur J Clin Invest. 2025 Apr;55(4):e70003. doi: 10.1111/eci.70003. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Eur J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 39937036 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the health and economic impact of pharmacologic therapies for MASLD in the United States.J Hepatol. 2025 Jul;83(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2025.01.009. Epub 2025 Jan 18. J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39832655
-
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A story of muscle and mass.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 May 28;31(20):105346. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.105346. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40495947 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in People With Diabetes: The Need for Screening and Early Intervention. A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association.Diabetes Care. 2025 Jul 1;48(7):1057-1082. doi: 10.2337/dci24-0094. Diabetes Care. 2025. PMID: 40434108 Review.
References
-
- Cusi K., Abdelmalek M.F., Apovian C.M., Balapattabi K., Bannuru R.R., Barb D., Bardsley J.K., Beverly E.A., Corbin K.D., ElSayed N.A., et al. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in People with Diabetes: The Need for Screening and Early Intervention. A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2025;48:1057–1082. doi: 10.2337/dci24-0094. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources