Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain
- PMID: 40869448
- PMCID: PMC12386564
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14165623
Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain
Abstract
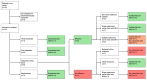
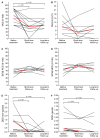
Background: Kidney-related pain can be chronic, disabling and negatively impact quality of life. In this prospective case series, we assessed whether a stepwise multidisciplinary treatment protocol, originally developed to treat ADPKD-related pain, can provide significant pain relief in non-ADPKD patients with kidney-related pain. Methods: Patients were eligible if they had incapacitating kidney-related pain with a visual analogue scale (VAS) score ≥50 out of 100, lasting ≥3 months and with insufficient response to previous treatments. The main exclusion criterion was ADPKD. Treatment options were, in order when indicated, nonpharmacological treatments, analgesics, cyst aspiration and fenestration, nerve blocks and nephrectomy. The effect of treatment on pain was investigated by means of VAS scores, defined daily dose of pain medication and quality-of-life scores. Results: Twelve patients (67% female, median age 50 [IQR: 36-59] years), with a median duration of pain of 1.9 [1.0-4.7] years, were included. In 50% of cases, chronic pain remained after an acute episode of kidney stones. Median follow-up after treatment was 3.8 [IQR: 2.5-4.4] years. The VAS before treatment (70 (48-90)) was reduced at short-term (35 [28-53], p = 0.01) and long-term follow-up (40 [38-53], p = 0.01). In addition, the defined daily dose of both opioids and non-opioids was reduced at short-term follow-up (p = 0.04 and 0.04, respectively) as well as at long-term follow-up (p = 0.03 and p = 0.02, respectively). Conclusions: We found that our multidisciplinary treatment protocol is effective in achieving sustained pain relief as well as a reduction in the use of pain medication in non-ADPKD patients with chronic, refractory kidney-related pain.
Keywords: kidney disease; kidney-related pain; nerve blocks; pain; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

