Exploring Cloned Disease Resistance Gene Homologues and Resistance Gene Analogues in Brassica nigra, Sinapis arvensis, and Sinapis alba: Identification, Characterisation, Distribution, and Evolution
- PMID: 40869898
- PMCID: PMC12385795
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16080849
Exploring Cloned Disease Resistance Gene Homologues and Resistance Gene Analogues in Brassica nigra, Sinapis arvensis, and Sinapis alba: Identification, Characterisation, Distribution, and Evolution
Abstract
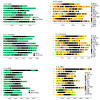
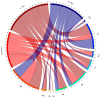
This study identifies and classifies resistance gene analogues (RGAs) in the genomes of Brassica nigra, Sinapis arvensis and Sinapis alba using the RGAugury pipeline. RGAs were categorised into four main classes: receptor-like kinases (RLKs), receptor-like proteins (RLPs), nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) proteins and transmembrane-coiled-coil (TM-CC) genes. A total of 4499 candidate RGAs were detected, with species-specific proportions. RLKs were the most abundant across all genomes, followed by TM-CCs and RLPs. The sub-classification of RLKs and RLPs identified LRR-RLKs, LRR-RLPs, LysM-RLKs, and LysM-RLPs. Atypical NLRs were more frequent than typical ones in all species. Atypical NLRs were more frequent than typical ones in all species. We explored the relationship between chromosome size and RGA count using regression analysis. In B. nigra and S. arvensis, larger chromosomes generally harboured more RGAs, while S. alba displayed the opposite trend. Exceptions were observed in all species, where some larger chromosomes contained fewer RGAs in B. nigra and S. arvensis, or more RGAs in S. alba. The distribution and density of RGAs across chromosomes were examined. RGA distribution was skewed towards chromosomal ends, with patterns differing across RGA types. Sequence hierarchical pairwise similarity analysis revealed distinct gene clusters, suggesting evolutionary relationships. The study also identified homologous genes among RGAs and non-RGAs in each species, providing insights into disease resistance mechanisms. Finally, RLKs and RLPs were co-localised with reported disease resistance loci in Brassica, indicating significant associations. Phylogenetic analysis of cloned RGAs and QTL-mapped RLKs and RLPs identified distinct clusters, enhancing our understanding of their evolutionary trajectories. These findings provide a comprehensive view of RGA diversity and genomics in these Brassicaceae species, providing valuable insights for future research in plant disease resistance and crop improvement.
Keywords: Brassicaceae; homologues; phylogenetic; resistance gene analogues; weed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Rcr12, a single dominant clubroot resistance gene near Rcr6 on chromosome B3 of Brassica nigra.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 18;25(1):925. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06947-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40681976 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of disease resistance genes in Brassica carinata.Plant Genome. 2025 Sep;18(3):e70087. doi: 10.1002/tpg2.70087. Plant Genome. 2025. PMID: 40765494 Free PMC article.
-
RGAugury: a pipeline for genome-wide prediction of resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in plants.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 2;17(1):852. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3197-x. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27806688 Free PMC article.
-
Frontiers in Dissecting and Managing Brassica Diseases: From Reference-Based RGA Candidate Identification to Building Pan-RGAomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 25;21(23):8964. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238964. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharya I., Dutta S., Mondal S., Mondal B. Clubroot disease on Brassica crops in India. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2014;36:154–160. doi: 10.1080/07060661.2013.875064. - DOI
-
- Barbetti M.J., Li C.X., Banga S.S., Banga S.K., Singh D., Sandhu P.S., Singh R., Liu S.Y., You M.P. New host resistances in Brassica napus and Brassica juncea from Australia, China and India: Key to managing Sclerotinia stem rot (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) without fungicides. Crop Prot. 2015;78:127–130. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2015.09.004. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

