Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population
- PMID: 40869910
- PMCID: PMC12385629
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16080862
Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population
Abstract
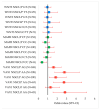
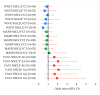
Background/Objectives: Non-syndromic cleft lip with or without palate (NSCL/P) is a common, multifactorial congenital anomaly. As genetic associations can be population-specific, this study aimed to investigate single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the VAX1, MAFB, and WNT3 genes for association with NSCL/P in a Japanese cohort. Methods: A case-control study was conducted with 310 Japanese patients with NSCL/P and 308 ethnically matched healthy controls from Aichi Gakuin Dental Hospital. We genotyped SNPs rs7078160 (VAX1), rs13041247 (MAFB), and rs3809857 (WNT3) using TaqMan assays. Associations were assessed using chi-squared tests, with results stratified by sex and corrected for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni method. Results: The VAX1 rs7078160 A allele was significantly associated with an increased risk for NSCL/P (OR = 1.67, p < 0.00001). The association was particularly strong in females (OR = 1.93, p < 0.00001) but not significant in males after correction. The MAFB rs13041247 variant showed a nominal protective association with the NSCLO subtype that was not significant after Bonferroni correction. No significant association was found for WNT3. A notable gene-gene interaction was observed, where carrying risk alleles for both VAX1 and MAFB significantly increased overall NSCL/P risk (OR = 2.65, p = 0.00008). Conclusions:VAX1 rs7078160 is a significant risk factor for NSCL/P in the Japanese population, with a pronounced female-specific effect. A synergistic interaction between VAX1 and MAFB elevates disease risk, whereas WNT3 was not implicated in this cohort. These findings underscore the population-specific genetic architecture of NSCL/P.
Keywords: Japanese population; MAFB; VAX1; WNT3; cleft lip with or without palate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wornom I.L., Will L.A., Burdi A.R., Berkowitz S., Breen M.L., Clarke-Sheehan N., Curtin V.M., D’Antonio L.L., Friedman C.D., Gleason A.T., et al. Core Curriculum for Cleft Lip/Palate and other Craniofacial Anomalies. In: Berkowitz S., editor. Cleft Lip and Palate. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2006. pp. 285–300. - DOI
-
- Yoshida K., Natsume N., Kinoshita H., Tsunoda N., Takahashi H., Kawai T. Experimental Study on Cleft Lip and/or Palate: Fetuses of A/J Mice in Uteri of F1 Hybrid Mothers Using Ovarian Transplantation. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1996;33:291–296. doi: 10.1597/1545-1569_1996_033_0291_esocla_2.3.co_2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

