The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Liobagrus huaiheensis (Teleostei: Siluriformes: Amblycipitidae): Characterization, Phylogenetic Placement, and Insights into Genetic Diversity
- PMID: 40870025
- PMCID: PMC12386135
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16080977
The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Liobagrus huaiheensis (Teleostei: Siluriformes: Amblycipitidae): Characterization, Phylogenetic Placement, and Insights into Genetic Diversity
Abstract
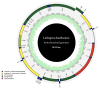
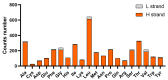
Background/Objectives: Liobagrus huaiheensis, an endemic fish in the Huaihe River basin, is a newly described species with limited molecular genetic research, hindering understanding of its evolutionary status, population structure, and genetic diversity. This study aimed to characterize its complete mitochondrial genome, clarify its phylogenetic position within Liobagrus, and assess its population genetic diversity. Methods: We obtained the complete mitogenome of L. huaiheensis (sourced from the Zhugan River) through sequencing, followed by detailed annotation of this genomic sequence. We analyzed its genomic structure, nucleotide composition, codon usage, and base asymmetry. Selection pressure on 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs) was evaluated using Ka/Ks ratios. Phylogenetic trees were generated by means of Bayesian inference (BI) and maximum likelihood (ML), using a dataset composed of 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs) from 37 species. Population genetic diversity was assessed using the cox1 gene. Results: The mitogenome is a 16,512 bp circular molecule encoding 37 genes and one control region, with a conserved structure typical of Liobagrus. It has high A + T content (55.74%) with A-preference and C-enrichment. All PCGs undergo purifying selection (Ka/Ks < 1). Phylogenetic analyses revealed L. huaiheensis is closest to L. obesus (100% support), with Liobagrus divided into three clades. The cox1 gene analysis showed low diversity (Hd = 0.656, π = 0.00171) and neutral evolution. Conclusions: This study fills the mitogenome data gap for L. huaiheensis, clarifies its evolutionary characteristics and phylogenetic position, and provides a basis for conservation genetics of Huaihe endemic fishes and molecular evolution research on Amblycipitidae.
Keywords: Liobagrus huaiheensis; genetic diversity; mitochondrial genome; phylogenetic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Li Z., Huang R.J., Tian H.J., Wu K.J., Wang C.Z., Meng X.L., Zhou C.J., Gu Q.H., Nie G.X. Investigation of fishery resources in Xinyang Reaches of the Huai River. Henan Fish. 2015;5:22—24+30.
-
- Sun Z.W., Ren S.J., Zhang E. Liobagrus chenghaiensis, a New Species of Catfish (Siluriformes: Amblycipitidae) from Yunnan, South China. Ichthyol. Exploit. Freshw. 2013;23:275–384.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- QN2021020/Youth Fund Project of Xinyang Agriculture and Forestry University
- 232300421273, 242300420175, 252102110075/Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province
- 23B240003, 24B240001/the Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province
- 252102110075/the Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

