Including the Magnitude Variability of a Signal in the Ordinal Pattern Analysis
- PMID: 40870312
- PMCID: PMC12385319
- DOI: 10.3390/e27080840
Including the Magnitude Variability of a Signal in the Ordinal Pattern Analysis
Abstract
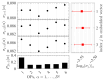
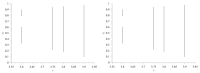
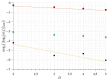
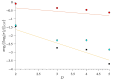
One of the most popular and innovative methods to analyse signals is by using Ordinal Patterns (OPs). The OP encoding is based on transforming a (univariate) signal into a symbolic sequence of OPs, where each OP represents the number of permutations needed to order a small subset of the signal's magnitudes. This implies that OPs are conceptually clear, methodologically simple to implement, and robust to noise, and that they can be applied to short signals. Moreover, they simplify the statistical analyses that can be carried out on a signal, such as entropy and complexity quantifications. However, because of the relative ordering, information about the magnitude of the signal at each timestamp is lost-this being one of the major drawbacks of this method. Here, we propose a way to use the signal magnitudes discarded in the OP encoding as a complementary variable to its permutation entropy. To illustrate our approach, we analyse synthetic trajectories from logistic and Hénon maps-with and without added noise-and real-world signals, including intracranial electroencephalographic recordings from rats in different sleep-wake states and frequency fluctuations in power grids. Our results show that, when complementing the permutation entropy with the variability in the signal magnitudes, the characterisation of these signals is improved and the results remain explainable. This implies that our approach can be useful for feature engineering and improving AI classifiers, as typical machine learning algorithms need complementary signal features as inputs to improve classification accuracy.
Keywords: feature extraction; ordinal patterns; permutation entropy; signal analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Healthcare workers' informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 27;8(8):CD015705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39189465 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Zanin M., Papo D., Sousa P.A., Menasalvas E., Nicchi A., Kubik E., Boccaletti S. Combining complex networks and data mining: Why and how. Phys. Rep. 2016;635:1–44. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.04.005. - DOI
-
- Shannon C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948;27:379–423. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x. - DOI
-
- Amigó J. Permutation Complexity in Dynamical Systems: Ordinal Patterns, Permutation Entropy and All That. Springer Science & Business Media; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2010.
-
- Lamberti P., Martin M., Plastino A., Rosso O. Intensive entropic non-triviality measure. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2004;334:119–131. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2003.11.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

