Relative Grip Strength as a Screening Indicator for Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data from KNHANES
- PMID: 40870518
- PMCID: PMC12388324
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61081473
Relative Grip Strength as a Screening Indicator for Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data from KNHANES
Abstract
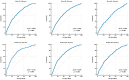
Background and Objectives: This study aimed to assess the association between relative grip strength (RGS) and metabolic syndrome (MetS) in Korean adults and to explore sex- and age-specific cutoff values for screening purposes. Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional study analyzed data from 12,072 Korean adults (aged 19-64 years) who participated in the 2017-2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed stratified by sex and age group, and participants were categorized into adequate (ARG) and low (LRG) RGS groups. Multivariable logistic regression was used to examine the association between RGS (as both categorical and continuous variables) and MetS, adjusting for lifestyle and behavioral covariates. Results: The RGS demonstrated moderate discriminatory power for MetS, with area under the curve (AUC) values ranging from 0.601 to 0.742. Age- and sex-specific cutoff values for RGS progressively decreased with age. Individuals in the LRG group had significantly higher odds of MetS across all age and sex groups. The LRG group had significantly greater odds of MetS in nearly all subgroups (e.g., women aged 20-39 years: odds ratio [OR] = 6.846; men: OR = 3.502). As a continuous variable, each 0.1-unit increase in RGS was associated with a 22.1-33.4% reduction in the odds of MetS (p < 0.001). Conclusions: RGS is inversely associated with MetS, particularly in women and younger adults. Although its discriminatory ability is moderate, the RGS may serve as a simple and accessible screening indicator to help identify individuals with an increased metabolic risk.
Keywords: grip strength index; lifestyle-related disease; metabolic screening; muscle assessment; population-based study; public health monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Red cell distribution width/albumin ratio as a marker for metabolic syndrome: findings from a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Oct 25;24(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01762-7. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39455980 Free PMC article.
-
Relative Excess Risk of Metabolic Syndrome Due to Interaction Between Handgrip Strength and Dietary Patterns Among Korean Youth.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 10;17(14):2282. doi: 10.3390/nu17142282. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732907 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-specific accuracy of lipid accumulation product index for the screening of metabolic syndrome in general adults: a meta-analysis and comparative analysis with other adiposity indicators.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jun 26;23(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02190-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38926783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noubiap J.J., Nansseu J.R., Lontchi-Yimagou E., Nkeck J.R., Nyaga U.F., Ngouo A.T., Tounouga D.N., Tianyi F.-L., Foka A.J., Ndoadoumgue A.L. Geographic Distribution of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components in the General Adult Population: A Meta-Analysis of Global Data from 28 Million Individuals. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;188:109924. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109924. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

