Functional Analysis of NPC2 in Alarm Pheromone Recognition by the Red Imported Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta (Formicidae: Solenopsis)
- PMID: 40870568
- PMCID: PMC12386980
- DOI: 10.3390/insects16080766
Functional Analysis of NPC2 in Alarm Pheromone Recognition by the Red Imported Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta (Formicidae: Solenopsis)
Abstract
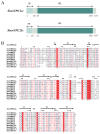
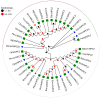
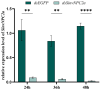
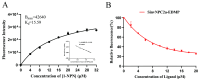
The red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) is a dangerous invasive insect. These ants rely on releasing an alarm pheromone, mainly composed of 2-ethyl-3,6-dimethylptrazine (EDMP), to warn nestmates of danger and trigger group defense or escape behaviors. This study found two NPC2 proteins in the ant antennae: SinvNPC2a and SinvNPC2b. SinvNPC2a was highly expressed in the antennae; phylogenetic analysis also suggests that SinvNPC2 likely possesses conserved olfactory recognition functions. By knocking down the SinvNPC2a gene, we found that the electrophysiological response of ant antennae to EDMP became weaker. More importantly, ants lacking SinvNPC2a showed significantly reduced movement range and speed when exposed to EDMP, compared to normal ants not treated with RNAi. These ants did not spread out quickly. Furthermore, tests showed that the purified SinvNPC2a protein could directly bind to EDMP molecules. Computer modeling also showed that they fit together tightly. These findings provide direct evidence that the SinvNPC2a protein plays a key role in helping fire ants detect the EDMP alarm pheromone. It enables the ants to sense this chemical signal, allowing ant colonies to respond quickly. Understanding this mechanism improves our knowledge of how insects smell things. It also suggests a potential molecular target for developing new methods to control fire ants, such as using RNAi to block its function.
Keywords: NPC2; RNA interference; alarm pheromone; electroantennography; fluorescence competitive binding; red imported fire ant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

