The Influence of Mediterranean and Western Dietary Patterns on Sensory Perception and Taste Sensitivity: A Study Among University Students
- PMID: 40870739
- PMCID: PMC12385536
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14162827
The Influence of Mediterranean and Western Dietary Patterns on Sensory Perception and Taste Sensitivity: A Study Among University Students
Abstract
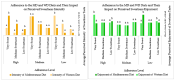
This study examines the relationship between dietary patterns, specifically the Mediterranean diet (MD) and the Western diet (WD), and sensory perception among nursing students at the University of Valladolid, Spain. The study aims to understand how these dietary patterns affect taste sensitivity and preferences, contributing to the fields of nutrition and sensory science. Materials and Methods: A total of 41 students participated in this study, following ethical guidelines. Food-grade materials such as refined salt, sucrose, monosodium glutamate, water, and breadsticks were used in sensory assessments. The study involved structured sensory evaluations along with dietary habit questionnaires. Sensory tests were conducted to measure taste perception, and statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0, with descriptive statistics and correlation analysis. Results: The findings revealed significant differences in taste perception across diet adherence levels. Specifically, higher adherence to the MD was associated with a higher perceived intensity and enjoyment of saltiness and umami, while a higher adherence to the WD showed a preference for sweetness. Significant correlations were found between diet adherence and taste enjoyment, with stronger positive associations for saltiness and umami under the MD. Conclusions: This study emphasized the impact of dietary habits on taste perception. Adherence to the MD enhanced sensitivity to moderate taste intensities, while adherence to the WD resulted in decreased perception at lower concentrations and heightened sensory responses at higher intensities. These results suggest that long-term dietary patterns influence taste receptor adaptation, potentially affecting food choices and overall health.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; Western diet; dietary adherence; food preferences; sensory perception; taste sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Shuaibu F.M., Gasma M.A., Abubakar A. Impacts of Food on Mind, Health, and Relationships: A Synthesis of Current Research. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2023;13:230–239. doi: 10.52403/ijhsr.20231128. - DOI
-
- Patil A., Singh N. From the Plate to the Mind: How Children’s Eating Habits Affect Their Physical and Mental Health. J. Neurol. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2023;5:40–53. doi: 10.46610/JNPMHN.2023.v05i02.005. - DOI
-
- Ruiz-Moreno E., Del Pozo de la Calle S., Valero Gaspar T., Ávila Torres J.M., Varela-Moreiras G. Estudio de Hábitos Alimentarios y Estilos de Vida de los Universitarios Españoles. Patrón de Consumo de Bebidas Fermentadas. Fundación Española de la Nutrición. 2013; pp. 1–32. [(accessed on 3 July 2024)]. Available online: http://www.fen.org.es/storage/app/media/imgPublicaciones/30092014131915.pdf.
-
- Kelishadi R., editor. Healthy Lifestyle: From Pediatrics to Geriatrics. Volume 3. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2022. Integrated Science. (print); ISBN 978-3-030-85357-0 (eBook) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

