Enhancing the Quality of Ginseng-Astragalus Medicinal Food Using Twin-Screw Extrusion
- PMID: 40870797
- PMCID: PMC12385580
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14162886
Enhancing the Quality of Ginseng-Astragalus Medicinal Food Using Twin-Screw Extrusion
Abstract
Twin-screw extrusion is a promising method to transform medicinal herbs into functional food ingredients. However, limited research has focused on the application of this technique to ginseng-astragalus compounds. In this study, the response surface methodology (RSM) was used to optimize the extrusion process (screw speed, temperature, and moisture content). The optimal parameters (208 rpm, 128 °C, 29%) significantly increased ginsenoside, polysaccharide, phenolic content, and antioxidant capacities (DPPH•, OH•, O2-•). Furthermore, extrusion improved the aroma profile while reducing bitterness, as revealed by electronic nose and electronic tongue, and PCA. The treated product also exhibited enhanced antibacterial activity. These findings demonstrate that twin-screw extrusion is an effective tool for developing medicinal food products with improved quality and biofunctionality. The response surface methodology model showed high reliability (R2 > 0.95) with prediction errors and relative standard deviations below 5%, confirming the robustness of the optimization.
Keywords: antioxidant properties; astragalus; bacteriostatic effects; chemical properties; flavor; ginseng; twin-screw extrusion.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





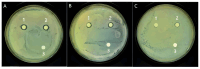
Similar articles
-
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Extrusion in Fortifying Rice Analogues With Dietary Fiber.J Food Sci. 2025 Aug;90(8):e70443. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70443. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40785441
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Plant-based protein extrusion optimization: Comparison between machine learning and conventional experimental design.Curr Res Food Sci. 2025 Jul 28;11:101157. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101157. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40792112 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

