The Use of Whey Powder to Improve Bread Quality: A Sustainable Solution for Utilizing Dairy By-Products
- PMID: 40870823
- PMCID: PMC12385520
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14162911
The Use of Whey Powder to Improve Bread Quality: A Sustainable Solution for Utilizing Dairy By-Products
Abstract
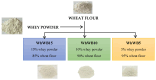
This paper aims to study the potential of whey, a by-product in the dairy industry, to be used as a sustainable and health-promoting ingredient in baking. In this regard, whey powder (WhF) was produced and incorporated into three composite flours consisting of wheat flour and whey powder in proportions of 5% (WhWF5), 10% (WhWF10), and 15% (WhWF15). These composite flours were then used to produce bread. The nutritional properties (proximate composition, macro and microelement content) and bioactive compounds (total polyphenols and antioxidant activity) were assessed for both the composite flours and the resulting breads. In addition, the rheological behavior of the dough was evaluated using the Mixolab system, while the microstructural characteristics and physical properties of the composite flours were analyzed using Small/Wide Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS/WAXS) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). Sensory evaluation of the breads was also performed. The results demonstrated a positive effect of the whey powder addition on the nutritional profile of both composite flours and bakery products, particularly through increased protein levels (25.24-37.77% in fortified flours vs. 11.26% in control; 16.64-18.89% in fortified breads vs. 14.12% in control) and enhanced mineral content (11.27-80.45% higher compared to white wheat bread), alongside a reduction in carbohydrate content. Bread fortified with 15% whey powder showed higher monolement with increases of 27.80% for K, 7.01% for Mg, and 28.67% for Ca compared to control bread without whey. The analysis of the Mixolab charts confirmed the progressive influence of whey powder on dough rheology. While water absorption remains high, other functional parameters, such as gluten quality, kneading capacity, and starch viscosity, were negatively affected. Nonetheless, the nutritional advantages and reduced retrogradation tendency may offset these drawbacks in the context of developing functional bakery products. Formulations containing 5-10% whey powder appear to offer an optimal balance between technological performance, nutritional quality, and sensory acceptance.
Keywords: MIXOLAB; bread; composite flours; nutritional; physical–chemical properties; sensory; wheat flour; whey powder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Verma D.K., Patel A.R., Tripathy S., Gupta A.K., Singh S., Shah N., Utama G.L., Chávez-González M.L., Zongo K., Banwo K., et al. Processing and Formulation Technology of Nutritional and Functional Food Products by Utilizing Cheese and/or Paneer Whey: A Critical Review. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024;36:103508. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2024.103508. - DOI
-
- Buchanan D., Martindale W., Romeih E., Hebishy E. Recent Advances in Whey Processing and Valorisation: Technological and Environmental Perspectives. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023;76:291–312. doi: 10.1111/1471-0307.12935. - DOI
-
- Minj S., Anand S. Whey Proteins and Its Derivatives: Bioactivity, Functionality, and Current Applications. Dairy. 2020;1:233–258. doi: 10.3390/dairy1030016. - DOI
-
- Mazorra-Manzano M.A., Martínez-García A., Torres-Llanez M.J., Ramírez-Suárez J.C., López-Franco Y.L., Brown-Bojórquez F., Teutle-Paredes J.G., Lugo-Sánchez M.E. Techno-Functional Properties of Mexican Cheese Whey Requesón Powder: Effects of Air-Convective Drying and Natural Gum Addition. Dairy. 2025;6:32. doi: 10.3390/dairy6040032. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

