A Partial Hydatidiform Mole in an Ovarian Ectopic Pregnancy: An Exceptional Occurrence
- PMID: 40870876
- PMCID: PMC12385901
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15162024
A Partial Hydatidiform Mole in an Ovarian Ectopic Pregnancy: An Exceptional Occurrence
Abstract
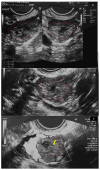
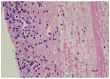
Background and Clinical Significance: Ovarian ectopic pregnancy (OEP) is a rare occurrence, and molar degeneration is even more exceptional. Differential diagnosis between a partial and complete hydatidiform mole is paramount as the complete type carries a higher risk of post-molar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Herein, we describe a case of a partial mole in an OEP (OPHM) with thorough investigations. Case Presentation: A 39-year-old woman presented at 6 weeks of amenorrhea with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Ultrasound showed no intrauterine pregnancy, but an ovarian cyst suspicious for OEP. The patient underwent surgical removal of the cyst. Histological diagnosis was suspicious for OPHM with only one abnormal villous. Immunohistochemistry for p57kip2 and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) were not conclusive. STR-based (Short Tandem Repeat) molecular technique demonstrated the chromosomal asset of 69,XXX, confirming the diagnosis of OPHM. The patient was fully monitored for 1 year with periodic measurements of beta-hCG levels. After that period, the patient was in good health and disease-free. Conclusions: Histologically, ancillary techniques might not be sufficient to confirm the diagnosis of a hydatidiform mole, especially if the tissue available is scarce. In this case, STR has been demonstrated an effective tool in defining the chromosomal asset, even in paraffin-embedded samples.
Keywords: Short Tandem Repeat (STR); ovarian ectopic pregnancy; partial hydatidiform mole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Møller P., Als-Nielsen A. Cas de Mole Hydatideuse Ovarienne. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1925;3:325–336. doi: 10.3109/00016342509157962. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

