Nanomedicine: The Effective Role of Nanomaterials in Healthcare from Diagnosis to Therapy
- PMID: 40871010
- PMCID: PMC12389108
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17080987
Nanomedicine: The Effective Role of Nanomaterials in Healthcare from Diagnosis to Therapy
Abstract
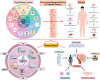
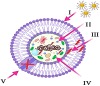
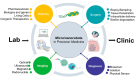
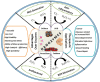
Nanotechnology is revolutionizing medicine by enabling highly precise diagnostics, targeted therapies, and personalized healthcare solutions. This review explores the multifaceted applications of nanotechnology across medical fields such as oncology and infectious disease control. Engineered nanoparticles (NPs), such as liposomes, polymeric carriers, and carbon-based nanomaterials, enhance drug solubility, protect therapeutic agents from degradation, and enable site-specific delivery, thereby reducing toxicity to healthy tissues. In diagnostics, nanosensors and contrast agents provide ultra-sensitive detection of biomarkers, supporting early diagnosis and real-time monitoring. Nanotechnology also contributes to regenerative medicine, antimicrobial therapies, wearable devices, and theranostics, which integrate treatment and diagnosis into unified systems. Advanced innovations such as nanobots and smart nanosystems further extend these capabilities, enabling responsive drug delivery and minimally invasive interventions. Despite its immense potential, nanomedicine faces challenges, including biocompatibility, environmental safety, manufacturing scalability, and regulatory oversight. Addressing these issues is essential for clinical translation and public acceptance. In summary, nanotechnology offers transformative tools that are reshaping medical diagnostics, therapeutics, and disease prevention. Through continued research and interdisciplinary collaboration, it holds the potential to significantly enhance treatment outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and usher in a new era of precise and personalized medicine.
Keywords: drug delivery system; healthcare; nanobots; nanomedicine; nanozyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Toumey C. Reading Feynman Into Nanotechnology: A Text for a New Science. Techne Res. Philos. Technol. 2008;12:33–168. doi: 10.5840/techne20081231. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

