Controlled Release of D-Limonene from Biodegradable Films with Enzymatic Treatment
- PMID: 40871185
- PMCID: PMC12389446
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17162238
Controlled Release of D-Limonene from Biodegradable Films with Enzymatic Treatment
Abstract
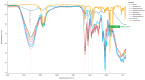
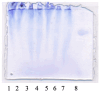
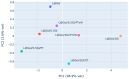
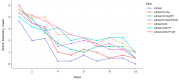
The instability of many volatile organic compounds (VOCs) limits their usage in different fragrance carriers and products. In scratch-and-sniff applications, VOCs are bound so strongly that release cannot happen without an external trigger. On the other hand, other fixatives like cyclodextrins release unstable volatile molecules too rapidly. We engineered biodegradable gelatin films whose release profile can be tuned by glycerol plasticization and alkaline protease degradation. Digitalized VOC release profiles acquired with the described near-real-time analysis toolkit are digital twins that replicate the behavior of the evaluated films in silico. Seven formulations were cast from 10% gelatin containing D-limonene, glycerol (5%, 20%), protease-C 30 kU mL-1, and samples with additional water to establish a higher hydromodule for protease catalytic activity. Release profiles were monitored for nine days at 23 ± 2 °C in parallel by metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) e-noses, gravimetric weight loss, and near-infrared measurements (NIR). These continuous measurements were cross-checked with gel electrophoresis, FTIR spectroscopy, hardness tests, and sensory intensity ratings. Results showed acceleration of VOC release by enzymatic treatment during the first days, as well as overall impact on the release profile. Differences in low and high glycerol films were observed, and principal component analysis of NIR spectra separated low and high glycerol groups, mirroring the MOS and FTIR data. Usability of MOS data was explored in comparison to more biased and subjective intensity results from sensory panel evaluation. Overall, the created toolkit showed good cross-checked results and enabled the possibility for close to real-time analysis for bio-based VOC carriers.
Keywords: D-limonene; MOS sensor; VOC; carriers; controlled release; digital twin; gelatin; protease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Machucho R., Ortiz D. The Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Business Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Applications, Organizational Challenges, and Ethical Considerations. Systems. 2025;13:264. doi: 10.3390/systems13040264. - DOI
-
- Shmelev S.E., Gilardi E. Corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance: The Impacts on Financial Returns, Business Model Innovation, and Social Transformation. Sustainability. 2025;17:1286. doi: 10.3390/su17031286. - DOI
-
- Sivasubramani S., Prodromakis T. Reaching New Frontiers in Nanoelectronics through Artificial Intelligence. Front. Nanotechnol. 2025;7:1627210. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2025.1627210. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

