Polymeric and Polymer-Functionalized Drug Delivery Vectors: From Molecular Architecture and Elasticity to Cellular Uptake
- PMID: 40871191
- PMCID: PMC12390004
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17162243
Polymeric and Polymer-Functionalized Drug Delivery Vectors: From Molecular Architecture and Elasticity to Cellular Uptake
Abstract
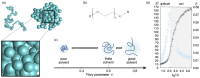
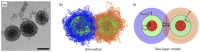
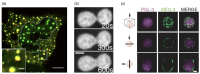
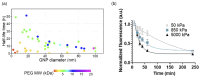
Polymers and polymer composites offer versatile possibilities for engineering the physico-chemical properties of materials on micro- and macroscopic scales. This review provides an overview of polymeric and polymer-decorated particles that can serve as drug-delivery vectors: linear polymers, star polymers, diblock-copolymer micelles, polymer-grafted nanoparticles, polymersomes, stealth liposomes, microgels, and biomolecular condensates. The physico-chemical interactions between the delivery vectors and biological cells range from chemical interactions on the molecular scale to deformation energies on the particle scale. The focus of this review is on the structure and elastic properties of these particles, as well as their circulation in blood and cellular uptake. Furthermore, the effects of polymer decoration in vivo (e.g., of glycosylated plasma membranes, cortical cytoskeletal networks, and naturally occurring condensates) on drug delivery are discussed.
Keywords: biomolecular condensates; cellular uptake; circulation times; drug delivery; hairy nanoparticles; linear chains; microgels; nanogels; passive endocytosis; polymer-grafted nanoparticles; star polymers; stealth liposomes; translocation.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Role of Cell Membrane-Vector Interactions in Successful Gene Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Aug 16;49(8):1486-93. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00200. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27459207
-
Exploring the Potentials of Hyaluronic Acid-coated Polymeric Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Treatment by Precision Drug Delivery, Tackling Drug Resistance, and Reshaping the Tumour Micro Environment.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(20):3960-3999. doi: 10.2174/0109298673302510240328050115. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38571347 Review.
-
Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles as a Smart Drug Delivery System for Peptide/Protein Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 19;17(6):797. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060797. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced rational design of polymeric nanoparticles for the controlled delivery of biologics.J Control Release. 2025 Aug 10;384:113940. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113940. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 40484283 Review.
References
-
- Liu W., Zhou X., Mao Z., Yu D., Wang B., Gao C. Uptake of hydrogel particles with different stiffness and its influence on HepG2 cell functions. Soft Matter. 2012;8:9235. doi: 10.1039/c2sm26001h. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

