Towards Enhanced Electrospinning of Alginate-Can Recent Strategies Overcome Limitations? A Review
- PMID: 40871202
- PMCID: PMC12390050
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17162255
Towards Enhanced Electrospinning of Alginate-Can Recent Strategies Overcome Limitations? A Review
Abstract
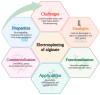
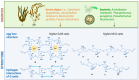
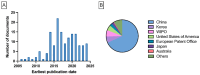
Electrospun alginate nanofibers are emerging as versatile materials for biomedical, environmental, and packaging applications due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and functional tunability. However, the direct electrospinning of alginate remains a significant challenge, mainly due to its polyelectrolytic nature, rigid chain structure, and limited chain entanglement. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent strategies developed to overcome these limitations, including polymer blending, chemical modification, the addition of surfactants, multi-fluid techniques, and process optimization. We systematically discuss the integration of nanofibers with functional agents such as microorganisms, bioactive compounds, plant extracts, and nanoparticles, highlighting their potential in wound healing, active packaging, bioremediation, and controlled release systems. This review also examines the scalability of alginate electrospinning, summarizing recent patents, industrial solutions, and challenges related to the standardization of the process. Key knowledge gaps are identified, including the need for long-term stability studies, structure-function correlations, green processing approaches, and expansion into novel application domains beyond healthcare. Addressing these research directions will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of alginate nanofibers as sustainable, high-performance materials for industrial use.
Keywords: alginate; biopolymers; electrospinning; functionalization; nanofibers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kogje M., Satdive A., Mestry S., Mhaske S.T. Biopolymers: A Comprehensive Review of Sustainability, Environmental Impact, and Lifecycle Analysis. Iran. Polym. J. (Engl. Ed.) 2025;n.a.:1–44. doi: 10.1007/s13726-024-01449-9. - DOI
-
- Abdu M.T., Abuhasel K.A., Alquraish M., Nagy S., Khodir S., Ali A.A. Selected Natural Fibers and Their Electrospinning. J. Polym. Res. 2023;30:1–35. doi: 10.1007/s10965-023-03699-2. - DOI
-
- Al-Attabi A., Ahmed A.T., Merza M.S., Shakier H.G., Zabibah R.S., Al-Hetty H.R.A.K., Baher H. Electrospinning in Food Packaging: Current Trend and Future Direction. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2024;37:571–584. doi: 10.1002/pts.2809. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

