COVID-19 Vaccination Still Makes Sense: Insights on Pneumonia Risk and Hospitalization from a Large-Scale Study at an Academic Tertiary Center in Italy
- PMID: 40871247
- PMCID: PMC12388399
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13081744
COVID-19 Vaccination Still Makes Sense: Insights on Pneumonia Risk and Hospitalization from a Large-Scale Study at an Academic Tertiary Center in Italy
Abstract
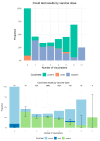
COVID-19 vaccines have revolutionized prevention and clinical management by reducing disease severity and mortality. However, their long-term impact on hospitalization is unclear. This retrospective study assessed whether vaccination status, timing, and number of vaccine doses influence the risk of hospitalization and COVID-19 pneumonia in a large cohort in Italy, several years after initial vaccine rollout. From 1 October 2023, to 2 February 2024, at Humanitas Research Hospital (Milan) and two affiliates, we recorded age, sex, comorbidities, vaccination status (number of doses and time since last dose), admission type (urgent vs. elective), and pneumonia diagnosis. Baseline health was quantified by the Charlson Comorbidity Index. Among 16,034 admissions (14,874 patients), vaccination data were available for 5743 cases: 40.8% were in the emergency setting and 59.2% were elective. Patients presented with pneumonia in 6.8% of cases. Laboratory results confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia occurred in 43.7% of pneumonia cases, with a 16.9% mortality. Patients with no vaccine dose had a higher proportion of COVID-19 pneumonia, while COVID-19 pneumonia rates were lower in individuals who had received more vaccine doses. There were no significant differences in COVID-19 pneumonia risk by timing of last vaccination. Moreover, hospitalized unvaccinated patients had overall more frequent emergency admissions (57.3%), while patients with three or more doses had about a ~40% emergency admission rate. COVID-19 positivity during hospitalization was highest in unvaccinated patients (90.7%) and declined with vaccination status. Vaccinated patients, especially those with multiple doses, had significantly lower COVID-19 pneumonia rates and emergency admissions. These findings suggest a possible protective effect of vaccination in modifying the clinical presentation and severity of illness among those who are hospitalized and support continued vaccination efforts for high-risk groups to reduce severe adverse outcomes.
Keywords: COVID-19; hospitalization; pneumonia; vaccination; vaccine hesitancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
RECOVID: Retrospective Observational Study of Renal Outcomes and Long-Term Mortality in Patients With COVID-19-Associated AKI, A Comparison Between Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Patients.Kidney Med. 2025 Jun 18;7(7):101020. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2025.101020. eCollection 2025 Jul. Kidney Med. 2025. PMID: 40607207 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic vaccination against human papillomaviruses to prevent cervical cancer and its precursors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 9;5(5):CD009069. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009069.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29740819 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

