Advances in Hydrodechlorination Technologies for Diclofenac Removal from Aqueous Systems
- PMID: 40871486
- PMCID: PMC12388549
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30163332
Advances in Hydrodechlorination Technologies for Diclofenac Removal from Aqueous Systems
Abstract
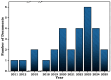
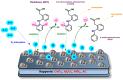
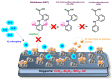
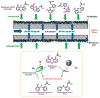
This review article describes the most recent studies carried out on the catalytic hydrodechlorination (HDC) of Diclofenac (DFC). In this context, the most commonly employed catalytic materials for the removal of DFC from aqueous matrices are reviewed, along with their main performance outcomes. Various strategies for the HDC of DFC are discussed, including conventional approaches that rely on molecular hydrogen as the electron donor, as well as emerging alternatives based on biocatalytic and electrocatalytic processes. Additionally, the optimized reaction conditions for each catalytic system are discussed, along with relevant kinetic models and mechanistic insights that contribute to a deeper understanding of the HDC of DFC. Future perspectives on the use of catalysts with alternative properties for DFC removal via HDC are also discussed, aiming to highlight potential applications in wastewater treatment and the broader field of heterogeneous catalysis.
Keywords: aqueous systems; catalysts; diclofenac; hydrodechlorination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alessandretti I., Rigueto C.V.T., Nazari M.T., Rosseto M., Dettmer A. Removal of Diclofenac from Wastewater: A Comprehensive Review of Detection, Characteristics and Tertiary Treatment Techniques. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:106743. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106743. - DOI
-
- Nunes B., Daniel D., Canelas G.G., Barros J., Correia A.T. Toxic Effects of Environmentally Realistic Concentrations of Diclofenac in Organisms from Two Distinct Trophic Levels, Hediste Diversicolor and Solea Senegalensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020;231:108722. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108722. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

