RetinoDeep: Leveraging Deep Learning Models for Advanced Retinopathy Diagnostics
- PMID: 40871882
- PMCID: PMC12390166
- DOI: 10.3390/s25165019
RetinoDeep: Leveraging Deep Learning Models for Advanced Retinopathy Diagnostics
Abstract
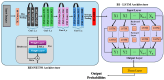
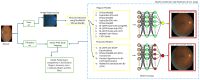
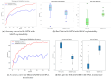
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), a leading cause of vision loss worldwide, poses a critical challenge to healthcare systems due to its silent progression and the reliance on labor-intensive, subjective manual screening by ophthalmologists, especially amid a global shortage of eye care specialists. Addressing the pressing need for scalable, objective, and interpretable diagnostic tools, this work introduces RetinoDeep-deep learning frameworks integrating hybrid architectures and explainable AI to enhance the automated detection and classification of DR across seven severity levels. Specifically, we propose four novel models: an EfficientNetB0 combined with an SPCL transformer for robust global feature extraction; a ResNet50 ensembled with Bi-LSTM to synergize spatial and sequential learning; a Bi-LSTM optimized through genetic algorithms for hyperparameter tuning; and a Bi-LSTM with SHAP explainability to enhance model transparency and clinical trustworthiness. The models were trained and evaluated on a curated dataset of 757 retinal fundus images, augmented to improve generalization, and benchmarked against state-of-the-art baselines (including EfficientNetB0, Hybrid Bi-LSTM with EfficientNetB0, Hybrid Bi-GRU with EfficientNetB0, ResNet with filter enhancements, Bi-LSTM optimized using Random Search Algorithm (RSA), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), and a standard Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)), using metrics such as accuracy, F1-score, and precision. Notably, the Bi-LSTM with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) outperformed other configurations, achieving superior stability and generalization, while SHAP visualizations confirmed alignment between learned features and key retinal biomarkers, reinforcing the system's interpretability. By combining cutting-edge neural architectures, advanced optimization, and explainable AI, this work sets a new standard for DR screening systems, promising not only improved diagnostic performance but also potential integration into real-world clinical workflows.
Keywords: EfficientNetB0; SHAP explainability; SPCL transformer; ant colony optimization; bidirectional LSTM; data augmentation; diabetic retinopathy; particle swarm optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- Venkatesh R., Gandhi P., Choudhary A., Kathare R., Chhablani J., Prabhu V., Bavaskar S., Hande P., Shetty R., Reddy N.G., et al. Evaluation of Systemic Risk Factors in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus for Detecting Diabetic Retinopathy with Random Forest Classification Model. Diagnostics. 2024;14:1765. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161765. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abushawish I.Y., Modak S., Abdel-Raheem E., Mahmoud S.A., Hussain A.J. Deep Learning in Automatic Diabetic Retinopathy Detection and Grading Systems: A Comprehensive survey and comparison of methods. IEEE Access. 2024;12:84785–84802. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3415617. - DOI
-
- Paranjpe M.J., Kakatkar M.N. Review of methods for diabetic retinopathy detection and severity classification. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2014;3:619–624. doi: 10.15623/ijret.2014.0303115. - DOI
-
- van der Heijden A.A., Nijpels G., Badloe F., Lovejoy H.L., Peelen L.M., Feenstra T.L., Moons K.G., Slieker R.C., Herings R.M., Elders P.J., et al. Prediction models for development of retinopathy in people with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and external validation in a Dutch primary care setting. Diabetologia. 2020;63:1110–1119. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05134-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

