Dendritic Cells and Their Crucial Role in Modulating Innate Lymphoid Cells for Treating and Preventing Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 40872304
- PMCID: PMC12389142
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens14080794
Dendritic Cells and Their Crucial Role in Modulating Innate Lymphoid Cells for Treating and Preventing Infectious Diseases
Abstract
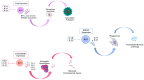
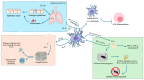
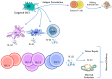
Two key players in the immune system, dendritic cells (DCs) and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), interact in a crucial way to fight infectious diseases. DCs play a key role in recognizing pathogens, and ILCs respond to cytokines released by DCs. This response triggers the production of specific effector cytokines that help control pathogens and maintain the body's barrier integrity. DCs have various receptors, including Toll-like receptors (TLRs), that detect microbial components and trigger immune responses. Likewise, ILCs act as essential initial responders in the immune system in viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections. Successfully managing diseases caused by pathogens mainly depends on the combined actions of DCs and ILCs, which work to suppress and eliminate pathogens. DCs also play a crucial role in activating innate and adaptive immune cell subsets, including ILCs. Furthermore, the use of DCs in developing vaccines and immunotherapy for cancers, along with the dedication of many researchers to improve immune responses through DCs, has increased interest in the potential of DC therapies for treating and preventing infectious diseases. This review examines approaches that may enhance DC vaccines and boost anti-infection immune responses by fostering better interactions of DCs with ILCs.
Keywords: dendritic cells; infectious diseases; innate lymphoid cells.
Conflict of interest statement
B.W.B. is the Chief Executive Officer of ImmunoCeutica Inc. (ICI), which is dedicated to the research and development of immunoceuticals. B.W.B. serves as a scientific advisor for the Canadian COVID Care Alliance (CCCA), Taking Back Our Freedoms (TBoF). Neither ICI, CCCA, nor TBoF were involved in any way with this manuscript and the research it describes. B.W.B. has received honoraria for speaking engagements and has given paid expert testimony in service to courts for his expertise in viral immunology. The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest to declare. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Innate lymphoid cells, immune functional dynamics, epithelial parallels, and therapeutic frontiers in infections.Int Rev Immunol. 2025;44(5):245-272. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2025.2490233. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Int Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40242974 Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Interactions Between the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1476:297-308. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-85340-1_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40622548 Review.
-
Trained ILCs confer adaptive immunity-independent protection against influenza.J Virol. 2025 Aug 4:e0053225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00532-25. Online ahead of print. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40757858
-
Use of CRISPR/CAS9 Technologies to Study the Role of TLR in Dendritic Cell Subsets.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2700:77-92. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3366-3_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37603175
References
-
- Karimi K., Boudreau J.E., Fraser K., Liu H., Delanghe J., Gauldie J., Xing Z., Bramson J.L., Wan Y. Enhanced antitumor immunity elicited by dendritic cell vaccines is a result of their ability to engage both CTL and IFNγ-producing NK cells. Mol. Ther. 2008;16:411–418. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300347. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

