A Comprehensive Review: Bovine Respiratory Disease, Current Insights into Epidemiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Vaccination
- PMID: 40872728
- PMCID: PMC12390213
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci12080778
A Comprehensive Review: Bovine Respiratory Disease, Current Insights into Epidemiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Vaccination
Abstract
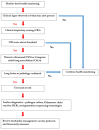
The aim of this comprehensive review is to synthesize current knowledge on bovine respiratory disease (BRD), enhance diagnostic strategies, and support effective prevention and management practises. BRD remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in cattle, driven by a complex interplay of viral and bacterial pathogens, host factors, environmental stressors, and management conditions. Its prevalence (2.1% to 20.2%) varies across geographical regions, age groups, and diagnostic methods. BRD leads to significant economic losses through direct impacts such as mortality, reduced growth rates, and lighter carcass weights, as well as indirect costs like market restrictions and long-term productivity declines. Diagnosing BRD is challenging due to its non-specific clinical signs and frequent subclinical presentations. Traditional diagnostic tools like clinical respiratory scoring (CRS) systems provide structure but suffer from low sensitivity and subjectivity. Behavioural monitoring shows promise by detecting early changes in feeding, movement, and social behaviours. Thoracic auscultation is widely used but limited in accuracy. Thoracic ultrasonography (TUS) stands out as a more sensitive method for detecting subclinical disease and correlating with growth outcomes. Combining CRS with TUS enhances early and accurate detection. Advancing diagnostic approaches is critical for improving animal health and minimizing economic losses in cattle production systems.
Keywords: bacterial pathogens; behaviour; bovine respiratory disease (BRD); clinical respiratory scores; diagnosis; thoracic ultrasonography (TUS); vaccination; viral pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Murray G.M., More S.J., Sammin D., Casey M.J., McElroy M.C., O’Neill R.G., Byrne W.J., Earley B., Clegg T.A., Ball H. Pathogens, patterns of pneumonia, and epidemiologic risk factors associated with respiratory disease in recently weaned cattle in Ireland. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2017;29:20–34. doi: 10.1177/1040638716674757. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources