Deficiency of IFNAR1 Increases the Production of Influenza Vaccine Viruses in MDCK Cells
- PMID: 40872812
- PMCID: PMC12390705
- DOI: 10.3390/v17081097
Deficiency of IFNAR1 Increases the Production of Influenza Vaccine Viruses in MDCK Cells
Abstract
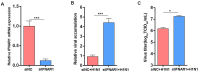
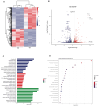
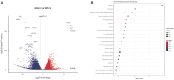
Cell culture-based influenza vaccines exhibit comparable safety and immunogenicity to traditional egg-based vaccines. However, improving viral yield remains a key challenge in optimizing cell culture-based production systems. Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells, the predominant cell line for influenza vaccine production, inherently activate interferon (IFN)-mediated antiviral defenses that restrict viral replication. To overcome this limitation, we employed CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology to generate an IFN alpha/beta receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1)-knockout (KO) adherent MDCK cell line. Viral titer analysis demonstrated significant enhancements in the yield of multiple vaccine strains (H1N1, H3N2, and type B) in IFNAR1-KO cells compared to wild-type (WT) cells. Transcriptomic profiling revealed marked downregulation of key interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs)-including OAS, MX2, and ISG15-within the IFNAR1-KO cells, indicating a persistent suppression of antiviral responses that established a more permissive microenvironment for influenza virus replication. Collectively, the engineered IFNAR1-KO cell line provides a valuable tool for influenza virus research and a promising strategy for optimizing large-scale MDCK cell cultures to enhance vaccine production efficiency.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; IFNAR1; MDCK cells; influenza vaccine; interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Iuliano A.D., Roguski K.M., Chang H.H., Muscatello D.J., Palekar R., Tempia S., Cohen C., Gran J.M., Schanzer D., Cowling B.J., et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet. 2018;391:1285–1300. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33293-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

