Melatonin Induces PERK-ATF4 Unfolded Protein Response and Apoptosis in Human Choriocarcinoma Cells
- PMID: 40873119
- PMCID: PMC12391747
- DOI: 10.1111/jpi.70072
Melatonin Induces PERK-ATF4 Unfolded Protein Response and Apoptosis in Human Choriocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
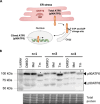
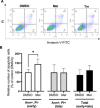
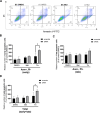
Melatonin, an indolamine primarily recognized for regulating circadian rhythms, has also demonstrated notable antitumoral properties. Melatonin induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, modulates autophagy, and promotes apoptosis in various tumors, including gastric, ovarian, cervical, oral tongue, colorectal, renal, hepatic, and bladder cancer. In placental choriocarcinoma, melatonin reduces cell viability and induces apoptosis by inhibiting autophagy and disrupting the mitochondrial membrane potential. However, its effects on ER stress and the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway remain unexplored. It is hypothesized here that the proapoptotic effects of melatonin in choriocarcinoma cells occur through the activation of the UPR pathway. The factors implicated in the UPR (PERK, IRE1ɑ, ATF6, GRP78, ATF4, CHOP, P-eIF2α) pathways were evaluated by Western blot, RT-qPCR, and flow cytometry in BeWo (human choriocarcinoma) cells treated with or without melatonin (1 mM). Melatonin significantly increased protein levels of GRP78 (p = 0.0329), IRE1α (p = 0.0394), p-eIF2α (p = 0.0439), ATF4 (p = 0.0267), CHOP (p = 0.0379), Bax and cleaved PARP but did not affect TRAF2 and NFkB protein levels nor XBP1 mRNA splicing. PERK knockdown, via siRNA, prevented the rise in GRP78, p-eIF2α/eIF2α, and ATF4 levels by melatonin. Additionally, melatonin increased early apoptosis in BeWo cells (p = 0.0371) and PERK knockdown increased the susceptibility of BeWo cells to apoptosis when treated with tunicamycin (p = 0.0359), suggesting that ER stress plays a role in BeWo cell survival. This study demonstrates that melatonin activates the PERK-ATF4-P-eIF2α-CHOP pathway and induces early apoptosis in BeWo cells, while PERK deficiency compromises cell survival under ER stress. Our findings suggest that modulating PERK-UPR signaling with melatonin could present a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer, including placental choriocarcinoma.
Keywords: BeWo cell; PERK pathway; apoptosis; choriocarcinoma; indolamine; melatonin; unfolded protein response.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Pineal Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling inhibits ERα expression in breast cancer.Neoplasia. 2025 Jul;65:101165. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2025.101165. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 40252311 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane induces cell morphology change and cell apoptosis by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress in glioblastoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1050. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14378-4. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597933 Free PMC article.
-
[Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jun 20;45(6):1240-1250. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40579137 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Protein-rich foods, sea foods, and gut microbiota amplify immune responses in chronic diseases and cancers - Targeting PERK as a novel therapeutic strategy for chronic inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Mar;255:108604. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108604. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38360205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Experimental Anti-Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6407. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136407. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

