Dual EGFR L858R and KRAS G12A Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 40873627
- PMCID: PMC12380001
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S531038
Dual EGFR L858R and KRAS G12A Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: KRAS mutations are typically mutually exclusive in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with the G12C mutation being the most common subtype. The coexistence of KRAS and EGFR mutations is exceedingly rare and is typically emerges as a secondary event following acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies. We presented a case of a newly diagnosed NSCLC patient harboring concurrent EGFR L858R and KRAS G12A mutations.
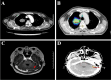
Case presentation: A 64-year-old male with a 30-pack-year smoking history presented with a 3-month history of progressive shortness of breath and chest tightness. Contrast-enhanced chest CT revealed a 5 cm spiculated mass in the right upper lobe, abutting the mediastinum, along with bronchial obstruction, right middle lobe atelectasis, and pleural effusion. A CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy confirmed lung adenocarcinoma. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) identified a c.2573T>G (p.L858R) mutation in exon 21 of the EGFR gene and a c.35G>C (p.G12A) mutation in exon 2 of the KRAS gene. The patient started first-line therapy with osimertinib combined with pemetrexed/nedaplatin, resulting in a transient partial response, significant resolution of pleural effusion, and partial regression of the primary tumor. However, disease progression occurred within 6 months, marked by the appearance of a new cerebellar metastasis, confirmed by MRI. The patient continued osimertinib maintenance therapy and underwent stereotactic radiotherapy for the brain lesion. Despite initial stabilization, pulmonary progression was observed 11 months after the start of treatment. Due to declining performance status and personal preferences, the patient declined further treatment and was lost to follow-up.
Conclusion: We report a rare case of treatment-naïve lung adenocarcinoma harboring concurrent KRAS G12A and EGFR L858R mutations. The patient achieved only transient disease control following treatment with a third-generation EGFR TKI combined with chemoradiotherapy. Further research to explore optimal therapeutic strategies for such complex molecular profiles is needed.
Keywords: EGFR; KRAS; concurrent mutation; non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2025 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Kinase Domain Duplication in Lung Adenocarcinoma with Sensitive Response to Afatinib: A Case Report and Literature Review.Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2025 Aug 12;16:97-105. doi: 10.2147/LCTT.S532278. eCollection 2025. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2025. PMID: 40821607 Free PMC article.
-
Miliary brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR (L858R) and CTNNB1 mutations.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Dec;14(34):3419-3420. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15144. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37920971 Free PMC article.
-
Triple reversal phenomenon in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma with prostate metastasis following hepatocellular carcinoma: a rare Case Report with diagnostic and therapeutic implications.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 16;12:1619466. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1619466. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40740944 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors for metastatic colorectal cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 27;6(6):CD007047. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007047.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28654140 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for the treatment of people with resected stage I to III non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR mutation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 27;5(5):CD015140. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015140.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40421698 Review.
References
-
- Kris MG, Gaspar LE, Chaft JE, et al. Adjuvant systemic therapy and adjuvant radiation therapy for stage I to IIIA completely resected non-small-cell lung cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology/Cancer Care Ontario clinical practice guideline update. J clin oncol. 2017;35(25):2960–2974. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.4401 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Planchard D, Feng PH, Karaseva N, et al. Osimertinib plus platinum-pemetrexed in newly diagnosed epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: safety run-in results from the FLAURA2 study. ESMO open. 2021;6(5):100271. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100271 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

