Nitrogen fertilizer improves Salix matsudana growth and soil qualities
- PMID: 40873710
- PMCID: PMC12378709
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1631852
Nitrogen fertilizer improves Salix matsudana growth and soil qualities
Abstract
Introduction: Soil contamination with heavy metals (e.g., Pb, Cd) poses severe environmental risks due to industrialization. Salix matsudana, a metal-tolerant woody plant, shows promise for phytoremediation, yet the synergistic role of nitrogen (N) fertilization in enhancing plant growth and soil remediation remains unclear. This study aims to elucidate how N fertilization optimizes S. matsudana's remediation efficiency.
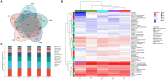
Methods: We applied integrated physiological and multi-omics approaches to assess N fertilization effects on S. matsudana growth, Pb/Cd uptake, and rhizosphere properties. Physiological metrics (biomass, metal accumulation) were combined with microbial community analysis (16S rRNA sequencing) and metabolomic profiling (LC-MS/GC-MS) of rhizosphere soils under varying N concentrations.
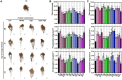
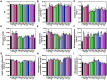
Results: High N levels significantly increased plant biomass and Pb/Cd accumulation. Microbial diversity shifted, with enriched metal-mobilizing taxa. Metabolomics revealed elevated organic acids, correlating with improved metal bioavailability and soil health.
Discussion: N fertilization synergistically enhances phytoremediation by: (1) stimulating plant growth and metal uptake, (2) reshaping rhizosphere microbiomes for metal mobilization, and (3) promoting chelating metabolite secretion. These findings provide actionable insights for optimizing N-assisted phytoremediation strategies.
Keywords: Salix matsudana; metabolomic; nitrogen fertilization; phytoremediation; rhizosphere microorganism.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Niu, Huang, Di, Su, Yuan, Wu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Adesemoye A. O., Torbert H. A., Kloepper J. W. (2010). Increased plant uptake of nitrogen from N-depleted fertilizer using plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Appl. Soil Ecol. 46, 54–58. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.06.010 - DOI
-
- Anup K. C., Rijal K., Sapkota R. P. (2015). Role of ecotourism in environmental conservation and socioeconomic development in Annapurna conservation area. Nepal. Int J Sust Dev World 22, 251–258. doi: 10.1080/13504509.2015.1005721, PMID: - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

