Taste Enhancement in Japanese Black Wagyu Beef Fed With Sake Lees: Insights From Metabolomic and Sensory Evaluations
- PMID: 40873968
- PMCID: PMC12378072
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70839
Taste Enhancement in Japanese Black Wagyu Beef Fed With Sake Lees: Insights From Metabolomic and Sensory Evaluations
Abstract
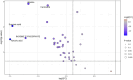
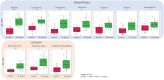
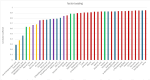
This study investigated the effects of sake lees (SL) supplementation on the taste characteristics of Japanese Black Wagyu beef. Analytical sensory testing and taste sensor analysis demonstrated significantly higher sweetness scores in the SL-fed group. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) identified increased levels of amino acids, nucleotides, and glucose 1-phosphate, compounds associated with sweetness and umami perception. Metabolomic pathway analysis indicated upregulation of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and purine metabolism in SL-fed cattle, suggesting enhanced energy metabolism and glycogen accumulation. These metabolic changes were consistent with sensory data, highlighting the potential of SL as a functional feed additive for improving beef palatability. This integrative approach combining sensory and chemical profiling provides new insight into taste enhancement mechanisms in livestock products.
Keywords: livestock; meat; omics analysis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abbiss, H. , Gummer J. P. A., Francki M., and Trengove R. D.. 2020. “Untargeted Liquid Chromatography‐Mass Spectrometry‐Based Metabolomics Analysis of Wheat Grain.” Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE 157: 60851. - PubMed
-
- Chen, X. , Mao Y., Liang R., et al. 2024. “LC‐MS‐Based Metabolomics Reveals Metabolite Dynamic Changes of Beef After Superchilling Early Post‐Mortem.” Food Research International 183: 114208. - PubMed
-
- Gauri, J. , Ashim Kumar B., Gorakh M., and Surendranath P. S.. 2024. “Bioactive Compounds in Meat: Their Roles in Modulating Palatability and Nutritional Value.” Meat and Muscle Biology 8, no. 1: 307.
-
- Immonen, K. , and Puolanne E.. 2000. “Variation of Residual Glycogen‐Glucose Concentration at Ultimate pH Values Below 5.75.” Meat Science 55, no. 3: 279–283. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

