Energy-efficient communication between IoMT devices and emergency vehicles for improved patient care
- PMID: 40875744
- PMCID: PMC12393732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330695
Energy-efficient communication between IoMT devices and emergency vehicles for improved patient care
Abstract
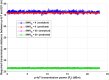
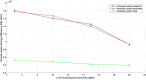
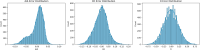
The rising integration of emergency healthcare services with the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) creates a significant opportunity to improve real-time communication between patients and emergency vehicles like ambulances. Fast and reliable data interchange is crucial in an emergency, especially for those with chronic conditions who rely on wearable IoMT devices to monitor vital health signs. However, establishing consistent communication in real-world conditions such as restricted signal strength, changing distances, and power constraints remains a major difficulty. This paper provides an intelligent communication framework that uses a one-dimensional deep convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) and Lagrange optimization techniques to improve energy efficiency and data transmission speeds. Unlike many earlier models, our technique takes into consideration real-world characteristics such as signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR), transmission power, and the distance between the ambulance and the patient's device. The primary goal is to identify the ideal communication distance for dependable, energy-efficient data transfer during urgent emergency situations. The findings show that the suggested system enhances communication reliability, consumes less energy, and increases the possible data rate. This framework accelerates, smartens, and strengthens emergency healthcare communication systems by combining deep learning and mathematical optimization. These findings contribute to the progress of intelligent healthcare infrastructure, opening the way for responsive and dependable emergency services that can adapt to changing conditions while maintaining high performance and patient safety.
Copyright: © 2025 Radwa Ahmed Osman. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Community First Responders' role in the current and future rural health and care workforce: a mixed-methods study.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024 Jul;12(18):1-101. doi: 10.3310/JYRT8674. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024. PMID: 39054745
-
Technologies for Interoperable Internet of Medical Things Platforms to Manage Medical Emergencies in Home and Prehospital Care: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 23;27:e54470. doi: 10.2196/54470. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39847768 Free PMC article.
-
An ensemble of deep representation learning with metaheuristic optimisation algorithm for critical health monitoring using internet of medical things.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 10;15(1):29241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15005-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40784985 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare workers' informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 27;8(8):CD015705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39189465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osman RA. Optimizing IoT communication for enhanced data transmission in smart farming ecosystems. Expert Syst Appl. 2025;265:125879. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125879 - DOI
-
- Al-Dhief FT, Latiff NMA, Malik NNNAbd, Salim NS, Baki MM, Albadr MAA, et al. A survey of voice pathology surveillance systems based on internet of things and machine learning algorithms. IEEE Access. 2020;8:64514–33. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.2984925 - DOI
-
- Reegu FA, Abas H, Jabbari A, Akmam R, Uddin M, Wu CM, et al. Interoperability requirements for blockchain-enabled electronic health records in healthcare: A systematic review and open research challenges. Secur Commun Netw. 2022;2022:9227343.
-
- Banumathy D, Khalaf OI, Tavera Romero CA, Raja PV, Sharma DK. Breast calcifications and histopathological analysis on tumor detection by CNN. Comput Syst Sci Eng. 2023;44:595–612.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

