In vitro screening of the open-access Pandemic Response Box reveals ESI-09 as a compound with activity against Echinococcus multilocularis
- PMID: 40876356
- PMCID: PMC12410356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2025.100609
In vitro screening of the open-access Pandemic Response Box reveals ESI-09 as a compound with activity against Echinococcus multilocularis
Abstract
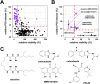
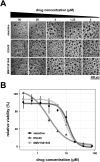
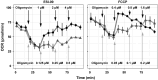
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is a life-threatening disease caused by the metacestode stage of the fox tapeworm Echinococcus multilocularis, primarily in the liver. Current drug treatments rely on benzimidazoles, which are not parasiticidal, requiring life-long therapy with significant side effects. Therefore, novel drug treatments are urgently needed. Drug repurposing offers a strategy to identify novel therapies against the neglected disease AE. We report on the in vitro screening of the Pandemic Response Box, an open-access compound library composed of 400 drug-like molecules assembled by Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) and the Drugs for Neglected Disease Initiative (DNDi), against E. multilocularis. An overview screen at 10 μM using the metacestode vesicle damage-marker release assay (based on release of phosphoglucose isomerase, PGI) and metacestode vesicle viability assay (based on ATP measurement) identified 37 active compounds. Reassessment in triplicates resulted in five active compounds (alexidine, carbendazim, ESI-09, MMV1581545, oxfendazole) displaying anti-metacestode activity. The parasiticidal activity of these five compounds was evaluated by ATP measurement in germinal layer cells. One compound, ESI-09, acted specifically against E. multilocularis (IC50 on metacestode vesicles 6.06 ± 3.18 μM by PGI release assay and 2.09 ± 0.56 μM by metacestode vesicle viability assay as well as an IC50 of 2.45 ± 0.86 μM on germinal layer cells) with a broad therapeutic window when compared to mammalian cell toxicity. Further experiments applying Seahorse technology and tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (TMRE) assay revealed that ESI-09 acts as a mitochondrial uncoupler in parasite cells. However, transmission electron microscopy showed no significant ultrastructural changes in parasite mitochondria, though increased secretion of extracellular vesicle-like structures between the tegument and the laminated layer was observed. In summary, screening of the Pandemic Response Box identified ESI-09 as a potential drug candidate for the treatment of AE. Further experiments are needed to evaluate the efficacy of ESI-09 in vivo.
Keywords: Alveolar echinococcosis; DNDi; Drug repurposing; Echinococcus mutlilocularis; MMV; Mitochondrial uncoupler.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest declaration I hereby confirm in the name of all listed authors (see below) for the manuscript „In vitro screening of the open-access Pandemic Response Box reveals ESI-09 as a compound with activity against Echinococcus multilocularis” that NONE of the authors have any conflict of interest. Thus, declarations of interest: none.
Figures










References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

