Novel Approach for Assessing Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes Prevention Trials Over a Fixed Time Interval
- PMID: 40877213
- PMCID: PMC12585163
- DOI: 10.2337/db25-0310
Novel Approach for Assessing Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes Prevention Trials Over a Fixed Time Interval
Abstract
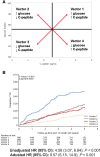
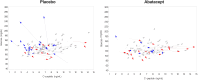
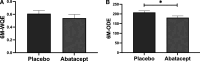
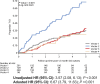
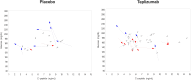
We evaluated whether a binary metabolic end point for change (Δ) from baseline to 1-year postrandomization could be useful in type 1 diabetes (T1D) prevention trials. Using 2-h oral glucose tolerance testing data from the stage 1 participants in the recent abatacept prevention trial and similar participants in the observational TrialNet Pathway to Prevention (PTP) study, we assessed Δmetabolic measures, plotted glucose and C-peptide response curves, and categorized vectors for Δ from baseline to 1 year as metabolic treatment failure versus success. Analyses were validated using the teplizumab prevention study. PTP participants with Δglucose >0 and ΔC-peptide <0 from baseline to 1 year were at substantially higher risk for stage 3 T1D than those with Δglucose <0 and ΔC-peptide >0 (P < 0.0001). Based on this, we compared placebo versus treatment groups in both trials for failure (Δglucose >0 with ΔC-peptide <0) versus success (Δglucose <0 with ΔC-peptide >0) after 1 year. Using this end point, a favorable metabolic impact of abatacept was found after 12 months of treatment. An analytic approach using a binary metabolic end point of failure versus success at a fixed time interval appears to detect treatment effects at least as well as standard primary end points with shorter follow-up.
Article highlights: Challenges in time to event type 1 diabetes (T1D) prevention trial design can yield negative results even for treatments that may actually improve disease pathology. We evaluated whether a binary metabolic end point for 12-month change from baseline to 1 year postrandomization could be useful in T1D prevention trials. This approach detected treatment effects at least as well as standard primary end points with shorter follow-up. Fixed interval metabolic end points should be used in combination with traditional T1D end points to better understand treatment effects of preventive agents.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Charles AAllard
- M01 RR00400/General Clinical Research
- U01 DK060782/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK085466/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133881/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 3-SRA-2015-27-Q-R/JDRF/United States
- R01 DK121929/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK133881/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI109565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK127382-012/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 2023-1422-S-B/SRA
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 82-2013-652/JDRF/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121843/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061035/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061016/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- U01 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2021258/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK121929/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- the Helmsley Charitable Trust, the Showalter Scholar Program
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1-SRA-2020-900-M-X/JDRF/United States
- K23 DK129799/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Alberta Diabetes Institute
- UM1AI109565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121843-01/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 62288/John Templeton Foundation
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK084565/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- U01 DK097835/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 3-SRA-2022-1186-S-B/Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2-SRA-2020-900-S-B/JDRF/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061029/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060916/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2-SRA-2018-609-Q-R/JDRF/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061037/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK097835/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061030/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800019C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- UL1 TR001872/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

