The role of the unfolded protein response pathway in bone homeostasis and potential therapeutic target in cancer-associated bone disease
- PMID: 40877255
- PMCID: PMC12394429
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-025-00457-6
The role of the unfolded protein response pathway in bone homeostasis and potential therapeutic target in cancer-associated bone disease
Abstract
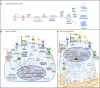
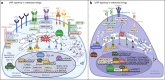
The unfolded protein response pathway is an evolutionarily conserved cytoprotective signaling cascade, essential for cell function and survival. Unfolded protein response signaling is tightly integrated with bone cell differentiation and function, and chronic unfolded protein response activation has been identified in bone disease. The unfolded protein response has been found to promote oncogenesis and drug resistance, raising the possibility that unfolded protein response modulators may have activity as anti-cancer agents. Cancer-associated bone disease remains a major cause of morbidity for patients with multiple myeloma or bone-metastatic disease. Understanding the critical role of unfolded protein response signaling in cancer development and metastasis, as well as its role in bone homeostasis, may lead to novel mechanisms by which to target cancer-associated bone disease. In this review, we summarize the current research delineating the roles of the unfolded protein response in bone biology and pathophysiology, and furthermore, review unfolded protein response modulating agents in the contexts of cancer and cancer-associated bone disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT: a review of diagnostic and prognostic features in multiple myeloma and related disorders.Clin Exp Med. 2015 Feb;15(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s10238-014-0308-3. Epub 2014 Sep 14. Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25218739
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Protein-rich foods, sea foods, and gut microbiota amplify immune responses in chronic diseases and cancers - Targeting PERK as a novel therapeutic strategy for chronic inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Mar;255:108604. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108604. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38360205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hebert, D. N. & Molinari, M. In and out of the ER: protein folding, quality control, degradation, and related human diseases. Physiol. Rev.87, 1377–1408 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.13, 89–102 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Wu, J. & Kaufman, R. J. From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ.13, 374–384 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

