Natural compounds attenuate combined chromium and arsenic-induced oxidative stress and nephritic apoptosis by activating the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling and associated xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes
- PMID: 40877299
- PMCID: PMC12394698
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13969-2
Natural compounds attenuate combined chromium and arsenic-induced oxidative stress and nephritic apoptosis by activating the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling and associated xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes
Abstract
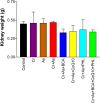
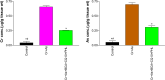
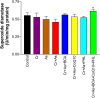
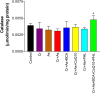
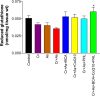
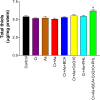
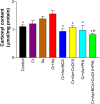
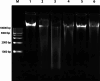
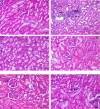
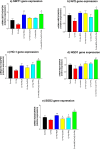
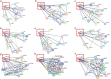
Chromium (Cr) and arsenic (As) pose a threat to the exposed population, leading to various renal ailments. Although individual toxicity has been well investigated, little is known about their combined effects. In light of the mounting concern over the environmental impact of heavy metals, the current study investigated the potential benefits of the selected nutraceuticals, i.e., biochanin-A (BCA), coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), and phloretin (PHL) in combined Cr + As intoxicated Swiss albino mice, providing a comprehensive understanding of the mechanism of action. During the two-week investigation, Cr (75 ppm) and As (100 ppm) were given orally to induce renal toxicity, and were simultaneously treated with BCA (50 mg/kg), CoQ10 (10 mg/kg), and PHL (50 mg/kg) intraperitoneally. The Cr + As-treated group showed an increase in kidney somatic index, metal burden, protein carbonylation, and malondialdehyde, along with a decrease in the activity of (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione-S-transferase, reduced glutathione, and total thiol). Furthermore, DNA degradation, histology, and altered SIRT1/Nrf2/HO‑1/NQO1/SOD2/CYP1A1/KEAP1/CAS-8, and CAS-3 gene expressions corroborated the above findings. Alternatively, co-treatment with the selected antioxidants reversed the above mentioned parameters, highlighting the protective effects of these compounds against Cr + As-induced oxidative damage. Nrf2, a key player in this process, is responsible for the activation of the antioxidant response element and subsequent expression of antioxidant enzymes. We further investigated the possible interactions of BCA, CoQ10, and PHL with the antioxidant enzymes/proteins, SIRT1/Nrf2/KEAP1/HO-1/NQO1, using in silico studies. Our study offers new avenues for the future of chronic kidney disease treatment associated with Cr + As-induced exposure, providing a deeper understanding of the role of Nrf2 in this context.
Keywords: Arsenic; Biochanin-A; Chromium; Coenzyme Q10; Phloretin; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Pratush, A., Kumar, A. & Hu, Z. Adverse effect of heavy metals (As, pb, hg, and Cr) on health and their bioremediation strategies: a review. Int. Microbiol.21 (3), 97–106 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Hingston, J. A. et al. Leaching of chromated copper arsenate wood preservatives: a review. Environ. Pollut. 111 (1), 53–66 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Poonia, T., Singh, N. & Garg, M. Contamination of arsenic, chromium and fluoride in the Indian groundwater: a review, meta-analysis and cancer risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol.18, 2891–2902 (2021).
-
- Goswami, R. et al. Potential arsenic-chromium-lead Co-contamination in the hilly terrain of Arunachal pradesh, north-eastern india: genesis and health perspective. Chemosphere323, 138067 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

