The role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in weight regain treatment or prevention after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40877612
- PMCID: PMC12394290
- DOI: 10.1007/s40519-025-01770-z
The role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in weight regain treatment or prevention after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Weight regain (WR) and insufficient weight loss (WL) occur in 20-25% of patients after bariatric surgery due to various factors. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have shown promise in promoting WL; however, evidence regarding their effectiveness in managing WL and preventing WR post-bariatric surgery remains limited.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the role of GLP-1RAs in treating and preventing WR following bariatric surgery.
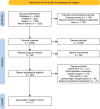
Methods: A systematic search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science for studies assessing the impact of GLP-1RAs on WR after bariatric surgery.
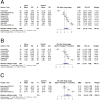
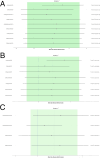
Results: Our search identified 27 original studies, with 10 included in the meta-analysis involving 769 participants (392 treated with GLP-1RAs). The mean age was 44.05 years, with 30.47% male. The time interval from surgery to the initiation of GLP-1RAs treatment ranged from 1.5 to 86.7 months, with treatment durations between 4 and 12 months. The analysis showed significantly greater WL in the GLP-1RAs group compared to placebo (SMD = 0.82, 95% CI 0.23 to 1.42). Subgroup analysis for treatment durations ≤ 6 months indicated a higher WL in the GLP-1RAs group (SMD = 0.79, 95% CI 0.25 to 1.34). Adverse events were primarily gastrointestinal, with nausea significantly more frequently in the GLP-1RAs group (OR = 2.01, 95% CI 1.24 to 3.27).
Conclusion: GLP-1RAs effectively promote WL among participants experiencing WR after bariatric surgery. Initiating GLP-1RAs therapy shortly after surgery may help prevent WR. Further research is warranted to explore long-term outcomes and optimize treatment protocols for this patient population.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; GLP-1RAs; Meta-analysis; Systematic review; Weight regain.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The quantity, quality and findings of network meta-analyses evaluating the effectiveness of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss: a scoping review.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jun 25:1-73. doi: 10.3310/SKHT8119. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40580049 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMJ. 2024 Jan 29;384:e076410. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076410. BMJ. 2024. PMID: 38286487 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide on heart rate among patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and pairwise and network meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Feb;26(2):548-556. doi: 10.1111/dom.15342. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 37860884
-
Discontinuing glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and body habitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Obes Rev. 2025 Aug;26(8):e13929. doi: 10.1111/obr.13929. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Obes Rev. 2025. PMID: 40186344
-
The Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists for Insufficient Weight Loss or Regain After Metabolic/Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obes Surg. 2025 Mar;35(3):1127-1134. doi: 10.1007/s11695-025-07723-w. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Obes Surg. 2025. PMID: 39910018
References
-
- Nedelcu M, Khwaja HA, Rogula TG (2016) Weight regain after bariatric surgery-how should it be defined? Surg Obes Relat Dis 12(5):1129–1130 - PubMed
-
- Yarigholi F et al (2022) Predictors of weight regain and insufficient weight loss according to different definitions after sleeve gastrectomy: a retrospective analytical study. Obes Surg 32(12):4040–4046 - PubMed
-
- Lautenbach A et al (2023) Sustained weight loss with semaglutide once weekly in patients without type 2 diabetes and post-bariatric treatment failure. Clin Obes 13(5):e12593 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

